Unit 5.2 Types of taxes
advertisement
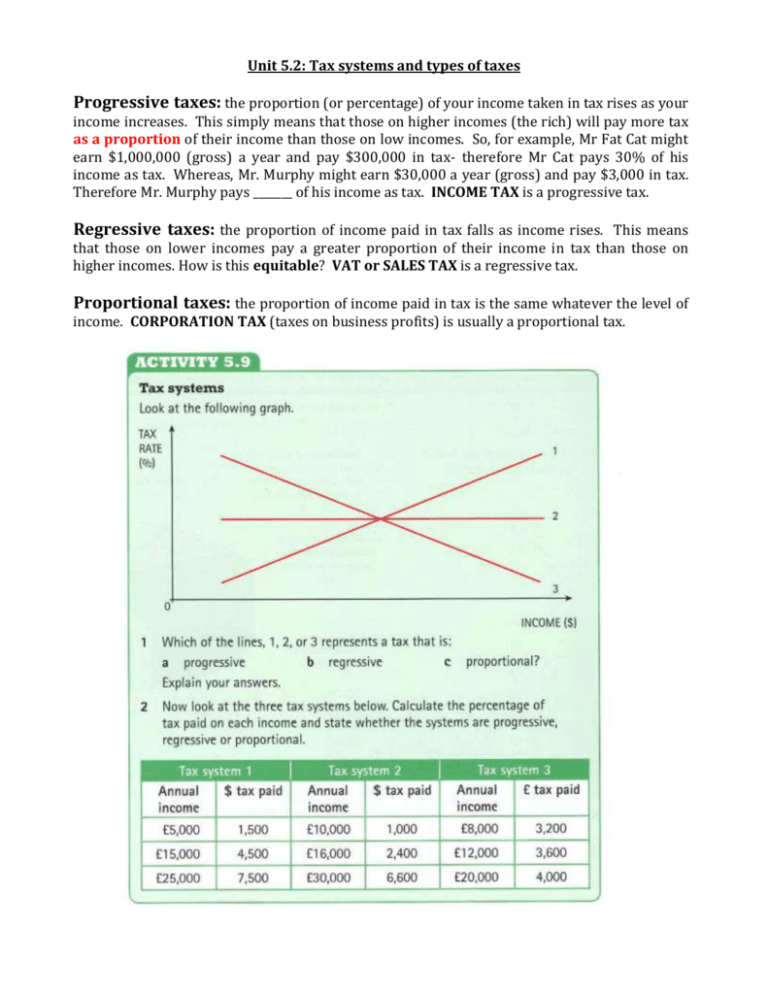
Unit 5.2: Tax systems and types of taxes Progressive taxes: the proportion (or percentage) of your income taken in tax rises as your income increases. This simply means that those on higher incomes (the rich) will pay more tax as a proportion of their income than those on low incomes. So, for example, Mr Fat Cat might earn $1,000,000 (gross) a year and pay $300,000 in tax- therefore Mr Cat pays 30% of his income as tax. Whereas, Mr. Murphy might earn $30,000 a year (gross) and pay $3,000 in tax. Therefore Mr. Murphy pays _______ of his income as tax. INCOME TAX is a progressive tax. Regressive taxes: the proportion of income paid in tax falls as income rises. This means that those on lower incomes pay a greater proportion of their income in tax than those on higher incomes. How is this equitable? VAT or SALES TAX is a regressive tax. Proportional taxes: the proportion of income paid in tax is the same whatever the level of income. CORPORATION TAX (taxes on business profits) is usually a proportional tax. Direct and Indirect taxes Direct taxes are taken directly from the person or firm who is responsible for paying them. They cannot be passed on to anyone else. Income tax is a direct tax as each worker must pay the tax from their income. Indirect taxes are taken indirectly from incomes when spending occurs. For example, indirect taxes such as sales tax or VAT are usually imposed upon producers but they will pass on most of the tax (the burden) on to consumers when they buy goods. Types of Direct Taxes: • • • • • Personal income tax- imposed on the income/earnings of individuals Corporation (or profits) tax – imposed upon the profits of businesses Capital gains tax- charged on profits made from the sale of shares, property even jewellery and other assets that have increased in value over time Wealth (e.g. inheritance and property) tax National (Social) Security contributions- these are imposed on both employers and employees and are specifically to raise funds for pensions, unemployment benefit and other benefits. Advantages of direct taxes • • • They are a major source of tax revenue Many are progressive and help to reduce inequalities in incomes after tax They take account of people’s ability to pay Disadvantages of direct tax • • • Income taxes can reduce work incentives Taxes on profits can reduce profit available to entrepreneurs to reinvest in their businesses High tax rates can cause tax evasion Types of Indirect taxes • • • • Value added tax (VAT)- this tax is added as a percentage of the selling price on goods and services sold. Some necessities are exempt from this tax. Excise duties – these are additional taxes charged on the quantity of tobacco/alcohol/petrol purchased. For example, 10cents a litre of fuel/$4 per pack of cigarettes/$1 per litre of wine Import tariffs – taxes specifically charged on imported goods entering a country User charges – charges for the use of toll roads, congestion charges (in London) Advantages of indirect taxes • • • They are cost effective to collect Anyone who buys goods and services will pay some indirect taxes They can be used to discourage consumption and production of harmful products Disadvantages of indirect tax • • • • The cost of collecting taxes falls to businesses They are regressive Tax revenues are less certain because they depend on spending patterns They add to price inflation






