Earthquakes!
advertisement

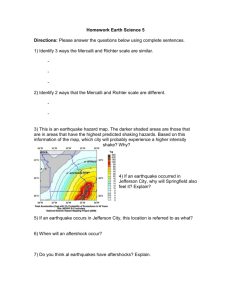
Warm Up 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. List the three types of volcanoes. What effects magma’s viscosity? Describe low viscous magma. High viscous magma. Which volcano produces the most violent eruptions? Which volcano has a short life span? What are convection currents and where do they occur? Where to plate tectonics take place? **Did you finish your VOLCANO homework??* **Set up NEW cornell notes on the next page! Write your objective and LEQ!!** Earthquakes! Objective: SWBAT describe the anatomy of an earthquake and relate to different types of plate boundaries. LEQ: How do the different aspects of an earthquake determine its severity? Unit 3: Table of Contents (1st & 3rd) Left Side Items Page Right Side Items Page Convection Article 20 Layers of Earth/Convection Currents CN 21 Layers of Earth Foldable 20 Plate Tectonics CN 23 Graham Cracker Lab 22 Volcano CN 25 Plate Boundaries Card Sort 22 Earthquake Anatomy CN 27 Volcano Stations 24 Earthquake Waves CN 29 Volcano Worksheet 24 Earthquake Presentation 26 Waves Mission Mastery 28 Unit 3: GEMS of Wisdom (1st & 3rd) Avid Strategy Page Convection Article 22 Layers of the Earth Foldable 22 Graham Cracker Lab 24 Plate Boundaries Card Sort 24 Volcano Stations 26 Volcano Worksheet 26 Earthquake Presentation 28 Waves Mission Mastery 30 W I C O R Unit 3: Table of Contents (2nd) Left Side Items Page Right Side Items Page Convection Article 22 Layers of Earth/Convection Currents CN 23 Layers of Earth Foldable 22 Plate Tectonics CN 25 Graham Cracker Lab 24 Volcano CN 27 Plate Boundaries Card Sort 24 Earthquake Anatomy CN 29 Volcano Stations 26 Earthquake Waves CN 31 Volcano Worksheet 26 Earthquake Presentation 28 Waves Mission Mastery 30 Unit 3: GEMS of Wisdom (2nd) Avid Strategy Page Convection Article 22 Layers of the Earth Foldable 22 Graham Cracker Lab 24 Plate Boundaries Card Sort 24 Volcano Stations 26 Volcano Worksheet 26 Earthquake Presentation 28 Waves Mission Mastery 30 W I C O R Agenda • • • • • • • Warm-up Objective & LEQ Activating Strategy Notes Group research Class presentations HW: Study for Friday’s quiz Activating Strategy • Imagine that you have just received news that Charlotte is preparing for an earthquake. If you had to prepare an emergency kit, what would you include? (Use complete sentences!) • Prepare for binder check • Get out volcano half-sheet to be collected Follow-up: Did you think of these things? • First aid kit and instruction booklet • Plastic tarp or a small tent • Emergency ("space") blankets and one sleeping bag for each family member • At least one gallon of bottled water per person, per day. For a 3-day supply, that adds up to three gallons of water per person • Enough canned or dried food for 3 days • Can opener • Flashlight (easily in reach) • Battery-powered radio • Spare batteries for everything (stored separately in waterproof bags) • Toilet paper, soap, toothpaste and toothbrushes, and other personal supplies • Multi-purpose dry chemical (Class ABC) fire extinguisher • Any important medicine and supplies for infants, elderly people, and others with special needs Haiti • • • • Earthquake example: Haiti, on January 12, 2010 How severe was this earthquake? 7.0 magnitude What happens with a 7.0 magnitude earthquake? What was the aftermath in Haiti? • http://www.iknowthat.com/mhscience/Earthquakes/earthqua ke_movie.html Japan • • • • Earthquake example: Japan, on March 11, 2011 How severe was this earthquake? What happens during a 9.0 magnitude earthquake? What actually happened in Japan? India • • • • Earthquake example: India, on September 18, 2011 How severe was this earthquake? 6.8 magnitude What happens? What actually happened? What is an earthquake? • An earthquake is the shaking of the ground due to the movements of tectonic plates What causes an Earthquake? Along a fault, energy builds up in a rock until it breaks and releases energy. This release of energy causes an earthquake. What is the Elastic Rebound Theory? • Gradual buildup, and release of stress and strain, between tectonic plates which leads to earthquakes What Causes Earthquakes? • As tectonic plates push, pull or scrape against each other, stress builds up along faults until the rocks finally move • A fault is a break in the Earth’s crust where plates slide, push or pull against each other What are the parts of an earthquake? The epicenter is the location on the surface of the Earth directly above the focus. Surface waves move outward from the epicenter. The focus of an earthquake is the point INSIDE the Earth where the earthquake starts. It is the place below the earth’s surface where the rocks tear, come apart, or collide. The fault is the break in the crust where the earthquake occurs, between two blocks of rock that have moved past each other. What is a Seismograph • Records ground movements caused by earthquakes, explosions, or other Earth-shaking phenomena. Magnitudes and Energy of Earthquakes Annual Numbers of EQs What’s the message? MOST of the energy is released by around 20 magnitude-7 and larger EQs every year. Seismic intensity is affected by rock type. Amplitude of oscillation Form a hypothesis about how would you expect the houses to react during an EQ. Seismic intensity is affected by rock type. Amplitude of oscillation increasing What is an Aftershock? • Smaller earthquake that occurs after a previous large earthquake, in the same area of the main shock. Earthquake Project • With your partner, read the article provided • You will create a poster that needs to include the following: • Table of information • Diagram of earthquake with the labeled parts (fault, epicenter, focus) • Definitions of the following vocabulary words: aftershock, fault, focus, epicenter, seismograph • You must include at least 3 colors!! • Create table on the copy paper which displays the following information about YOUR earthquake: • • • • • • Earthquake Location Date of Earthquake Magnitude Location of Epicenter Approximate Deaths Major destruction and damage • Draw and label the different parts of an earthquake • You have 15 minutes • http://library.thinkquest.org/TQ0311162/anatomy.htm • http://dsc.discovery.com/guides/planetearth/earthquake/inte ractive/interactive.html • http://larryferlazzo.edublogs.org/2011/01/10/the-best-sitesfor-learning-about-earthquakes/ • http://teacher.scholastic.com/activities/wwatch/earthquakes/ • http://www.sciencecourseware.com/virtualearthquake/VQua keExecute.html Exit Ticket 1. Draw and label diagram which represents an earthquake and its components. 2. What is an aftershock? 3. What records ground movements caused by earthquakes, explosions, or other Earth-shaking phenomena? 4. True or False: Seismic intensity (vibration) is greater on bed rock than on water-saturated sand and mud. 5. True or False: A 7.0 magnitude earthquake will always cause the same amount of damage, regardless of where the earthquake occurs (ex. Haiti vs. California)