Exam 1 Jeopardy
advertisement

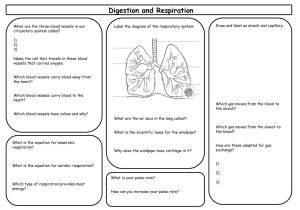
Hormones Structures and Respiration Diagrams Enzymes Misc. 10 10 10 10 10 20 20 20 20 20 30 30 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 40 50 50 50 50 50 Structures - 10 • Name the three parts of the small intestine in order. Nervous System – 10 • Duodenum • Jejunum • Ileum Structures - 20 • What is the structure that keeps the alveoli sterile? Structures – 20 • Macrophages Structures - 30 • What is the structure that induces coughing if anything touches it? • Where is this structure located? Structures – 30 • Carina • Top of the bronchi Structures - 40 • Name four accessory organs. Structures – 40 • • • • • • Teeth Tongue Pancreas Liver Gall Bladder Salivary Glands Structures - 50 • Trace a piece of food through the entire digestive tract. Include accessory organs and how they participate in digestion. Structures – 50 • • • • • • • • • • Mouth – teeth, tongue, salivary glands Esophagus Stomach – parietal, chief, enteroendocrine cells Duodenum – liver/gall bladder, pancreas Jejunum Ileum Cecum Colon Rectum Anus Hormones and Enzymes - 10 • What are two hormones produced by the pancreas? Hormones and Enzymes – 10 • Insulin • Glucagon Hormones and Enzymes - 20 • What are three proteases found at the brush border? Hormones and Enzymes – 20 • Trypsin • Chymotrypsin • Carboxypeptidase Hormones and Enzymes - 30 • Name two substances that digest fat and where they are active. Hormones and Enzymes – 30 • Lingual lipase – stomach • Bile – Duodenum • Pancreatic Lipase - Duodenum Hormones and Enzymes - 40 • What enzymes are involved in the digestion of proteins and how do they work? Hormones and Enzymes – 40 • Carboxypeptidase attacks from the carboxyl end • Aminopeptidase attacks from the amine end • Dipeptidase breaks didpeptides Hormones and Enzymes - 50 • Name five substances that inhibit gastric motility and secretion. Hormones and Enzymes – 50 • • • • • CCK Secretin Serotonin Somatostatin Gastric Inhibitory Peptide Respiration - 10 • What is the function of the upper respiratory system? Respiration – 10 • Filter • Heat • Humidify Respiration - 20 • Define total dead space. Respiration – 20 • Anatomical dead space and alveolar dead space Respiration - 30 • What is Henry’s law and why is it important in breathing? Respiration – 30 • Amount of gas dissolved in a liquid depends on solubility of gas, temperature of liquid, and partial pressure of the gas • Describes amount of dissolved O2 Respiration - 40 • Explain the importance of surfactant. Respiration – 40 • Reduces surface tension in lungs and keeps them from collapsing Respiration - 50 • What is the alveolar ventilation rate? Respiration – 50 • Frequency X (total volume – dead space) Diagrams - 10 • Draw an alveoli from the outside Diagrams – 10 Diagrams - 20 • Show/Explain the structures in the small intestine to increase surface area Diagrams – 20 Diagrams - 30 • Draw an alveoli from the inside Diagrams – 30 Diagrams - 40 • Diagram the process of HCl production Diagrams – 40 Diagrams - 50 • Draw the oxyhemoglobin curve and explain what will shift it to the right. Diagrams – 50 Misc. - 10 • What is your favorite example Dr. Selsby has given in class? Misc. – 10 • Saltine cracker experiment Misc. - 20 • Name one component of saliva Misc. – 20 • • • • • • • Mucus Water Ig A Lysozyme Lingual lipase Salivary amylase Electrolytes Misc. - 30 • How many oxygens can hemoglobin bind? Misc. – 30 • 4 Misc. - 40 • Describe the difference between peristalsis and segmentation Misc. – 40 • Peristalsis moves food along • Segmentation mixes food Misc. - 50 • Explain one connection between the respiratory system and the digestive system. Misc. – 50 • CO2 is required for HCl production