File
advertisement

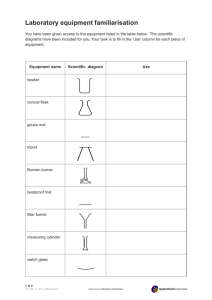
Name: _____________________ Aim: To observe the effect that the rate of cooling has on the size of crystals formed. Materials: Copper Sulphate 50 mL tap water Stirring rod 50 mL beakers 2 x evaporating dishes Bunsen burner Heatproof mat Gauze mat Tripod Styrofoam cup Crushed ice – to collect only when needed Hand lens – to collect only when needed IMPORTANT: Safety glasses and aprons MUST be worn throughout the duration of this practical. Method: 1. 2. 3. 4. Measure out 50 mL of water into a beaker. Add a small amount of copper sulphate into the beaker of water. Place the Bunsen burner on the heatproof mat. Light the Bunsen burner making sure that the hole is closed when you light it. Make sure to light the match before turning on the gas. 5. Place and tripod and gauze mat over the Bunsen burner. 6. Open the hole so that a working flame is observed. 7. Place the beaker carefully onto the gauze mat and stir the solution continuously. 8. Heat gently until the Copper Sulphate has dissolved. Add more Copper Sulphate to the solution and continue stirring. Continue this process until no further Copper Sulphate will dissolve. 9. Turn off the Bunsen burner. 10. Remove the beaker from the gauze mat and carefully pour the mixture evenly between the evaporation dish and the Styrofoam cup. 11. Place the evaporation dish onto the bed of crushed ice. 12. Leave the solutions for a couple of days to allow crystals to form. 13. Carefully pour out any remaining liquid leaving only the crystals behind. 14. Pour some of the crystals from the Styrofoam cup into the other evaporating dish. 15. Examine the crystals with a hand lens. Results: Draw a diagram of the crystals in each of the evaporating dishes, concentrating on their size and shape. Label the pictures as fast cooling or slow cooling. Discussion: Which dish contained the larger crystals – the one that cooled quickly or the one that cooled slowly? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Which type of igneous rock would you expect to have the larger crystals – those that form below the Earth’s surface (intrusive) or those that form above (extrusive)? Explain. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Conclusion: __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________