What is Science? - Year7Science2012
advertisement

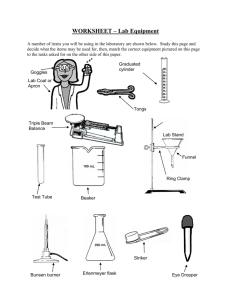
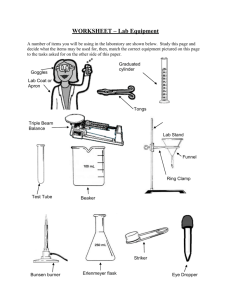
What is Science? Year 7 How many Sciences can you name? Quickly jot down as many as you can How many Sciences can you name? Commonly known ones: • Biology • Chemistry • Physics • Geology • Forensics • Psychology What are the skills needed to be a scientist? List at least 10 of them What are the skills needed to be a scientist? Did you get all of these? APPLY INFER OBSERVE MEASURE HYPOTHESISE ANALYSE PREDICT TEST CONCLUDE INTERPRET EVALUATE GRAPH CLASSIFY EXPERIMENT FIND LINKS Why do they need those skills? For 2 of your words Explain why a scientist needs that skill e.G Observant – Scientists need to observe because then they can see any changes that happen in an experiment. Why do they need those skills? All scientists need to be able to • Communicate with others • Solve problems • Think clearly In order to do these they must use their _________ Senses • What are the senses? ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ Senses • What are the senses? SEEING HEARING TOUCH SMELL TASTE Senses SEEING uses your HEARING uses your TOUCH uses your SMELL uses your TASTE uses your And these are all linked to your ________ by the ____________ system. Senses SEEING uses your EYES HEARING uses your EARS TOUCH uses your HANDS SMELL uses your NOSE TASTE uses your TONGUE And these are all linked to your BRAIN by the NERVOUS system. The Eye • Sees the world upside down The Ear • Helps us to balance The Skin • Reacts to temperature, humidity, pain The Nose • Affects the taste too The Tongue • Has lots of taste buds YOUR TASK • Choose ONE of the senses and write a journal reflecting on the job you perform each day and how you help people to do different things. (1 page) • Example – My name is Terry the tongue and I ……. YOUR TASK • Design a rap song, song or a poem based on the equipment you would find in the laboratory and why it is so important to use it safely. • 6 – 8 lines. Before we start… • Before prac – playing it safe in the lab (click view) • Matching game with equipment Practical 1 Blindfold partner 1. Pair up 2. Student A is blindfolded 3. Student B guides A around the room, taking care to tell A about obstacles 4. Students switch roles 5. Record what it felt like to be led and what you noticed about giving instructions in student booklet Practical 2 Mystery objects - touch 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Pair up Student A is blindfolded Student B selects three objects from the front Student A is to identify the objects passed to them by B. Student B records the results Students switch roles Practical 3 Mystery objects - smell 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Pair up Student A is blindfolded Student B selects three objects from the front Student A is to identify the objects held under their nose by B. Student B records the results Students switch roles Practical 4 Where does the sound come from? All students close their eyes Students to walk around the room When a sound is heard student point in the direction of sound Volunteer will record results Discuss Basketball video • Basketball • Watch the video and count how many times the white team passes the ball to each other. Observing - recording • Draw a map of the laboratory • Mark the safety equipment • Mark on the lab equipment Safety Why do we have safety rules? What rules do you know already? Watch safety video Design your own poster Before we start.. Before we start every practical we need to outline our AIM (What we hope to achieve) and our HYPOTHESIS (what we think might happen) Title = Boiling Water Practical Aim = Hypothesis = Before we start… Now we need to draw up a table for our results Attempts 1. 2. 3. 4. Time Taken (min/secs) Lets get started with….Laboratory Equipment You must find and place on your desk: • A beaker • Safety goggles • A heatproof mat • A pencil/pen and our workbooks • A measuring cylinder • Bunsen Burner • Gauze mat • Tripod • Boss • Retort stand Boiling Water Practical Method 1. Put on safety goggles and apron 2. Set up your Bunsen burner as practiced but leave burner UNLIT! (heat proof mat under Bunsen, Bunsen attached to gas) 3. Measure out 20mls of water into your beaker using your measuring cylinder 4. Light your Bunsen Burner then put tripod and gauze mat ontop. Boiling Water Prac (cont.) 5. Place beaker ontop of tripod (carefully) and start stopwatch 6. Once water begins to bubble stop timing. 7. Attempt steps 1-6 three more times and record the result in your table. 8. Draw a graph using the next slide as an example. Graphing our results The time taken for water to boil using a Bunsen Burner 5 4 Time Taken (Mins) 3 2 1 0 Atempt 1 Attempt 2 Attempt 3 Attempt 4 So what happened? Discussion 1. Why did we do this practical 3 times? 2. Did the time taken for the water to boil vary? Why/why not? 3. What conclusions can you draw from your results? Conclusion? Equipment – drawing and diagrams Can you match them up? Equipment – drawing and diagrams Can you identify the equipment from it’s diagram? Laboratory Equipment Name Drawing Test tube x Beaker x Gauze X Bunsen Burner X Heat proof mat X Tripod X Thermometer Filter funnel x Conical flask Boss, clamp & stand Measuring cylinder x Mirror Battery Lens Stopwatch x Diagram Using a Bunsen burner • Flame colours • Safety • Lighting the burner correctly Practical write -ups • Watch video • Read through guidelines What is needed in a write-up? Graphs List the types of graph that you know Did you get Bar chart Line graph Scatter graph Choosing the right graph In Science we nearly always use line graphs to illustrate our findings. Bar charts are used to show results from surveys OR when data is not numerical Scatter graphs are rarely used Measuring devices How many instruments can you name that measure… 1. Time 2. Length 3. Mass Time • • • • • • • • • • • Stopwatch Y Watch Y/N Sun N Clock Y/N Computer Y/N Stars/moon N Body clock N Phone Y/N Television N Sand timer N Fixture/timetable N Length • Ruler Y • Measuring tape Y • Trundle wheel Y/N • Walking/ pedometres N • Limbs/handspan/body parts N • Laser N Mass • Scale Y • Hefting Y/N • Beaker Y/N • Displacement method Y • Test tube N How could we test each of these? TASK - Outline a practical (Aim and hypothesis) that would allow data to be collected using each of these measuring devices. • E.g Time = Aim – To measure the time it would take a human to carry a washing machine 100m. Hypothesis – The heavier the washing machine, the greater the time taken to cover 100m. How could we test it further? TASK – for ONE of your outlined practical's, design a materials list, method, predict results (see me if confused!!) draw a graph or table and write a conclusion to test your practical. Units of measurement In Science we have an agreement to use universal units … SI units Measurement Unit Symbol Length Metre m Mass Kilogram kg Time Second s Temperature Degree celsius ◦C Volume Cubic metre m3 Temperature Practical • What measures temperature? • What could we measure the temperature of? • How can we control the temperature? • How many readings do we take? Practical circus • Measuring mass • Measuring volume • Measuring length • Measuring volume of irregular object • Measuring time