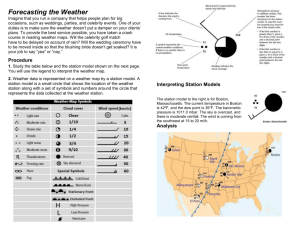
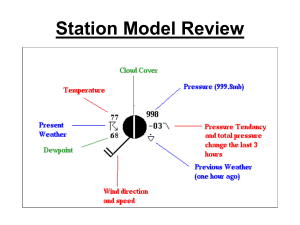
Atmospheric MoistureNotes
advertisement

Atmospheric Moisture & Clouds 1) Water vapor is the ________________________________________________________ Essentially all water on Earth is ________________________________ 2) Changing states requires _________________________________________________ Water has a __________________________ ++So a large amount of _________________________________as water changes temperature 3) The addition of heat:______________________________________________________ The removal of heat __________________________________________________ 4) Saturation – the maximum __________________________air can hold at ________________ Warm air can hold ________________________________than cool air 5) __________________________: Ratio of the air’s ________________________ compared with the __________________________________________ at that temperature and pressure 2 ways to change RH: ____________________________________________________ Higher temp: ________________ Lower temp: ________________ 6) Once air is saturated further cooling causes ________________________ (ex: dew, clouds) Condensation nuclei: Measured using a psychrometer 7) Dew Point – Depends on? For every 10° C increase in temp.: ________________________________________________ High dew points _______________________ Low dew point ______________________ 8) Dew point can found by using the RH When air temp. and dew point are close: __________________________________ When air temp. and dew point are far apart: _____________________________________ 9) Adiabatic Temperature Changes: When air expands: ______________ -When air is compressed: _______________ 10) Orographic: Frontal Wedging: Convergence: Convective: 11) Stable air _______________________ Unstable air ___________________ -Most stable occurs with a ____________________ which means air temp _________________ Stability & Weather: Stable air: _________________________ 12) Clouds Unstable air: ______________________________ Classified based on form and height Cirrus: _______________________________________ Cumulus: _________________________________________ Stratus: ___________________________________________________ Nimbus: _________________________________________________ Combinations of these are used to describe any cloud 13) Fog Cumulonimbus= ______________ Occurs when ___________________________________________________ Warm air moving over _________________________ (typical fog) (California ‘marine layer’) Cool air moving over __________________________ (smoke on the water) 14) Precipitation Cloud droplets______________________________ Must grow ____________________________ Most precipitation starts __________ Rain: __________________________________ Snow: Sleet: _____________________________________ Freezing rain: _______________________________________ Hail: ____________________________________________________