STUDY GUIDE
advertisement

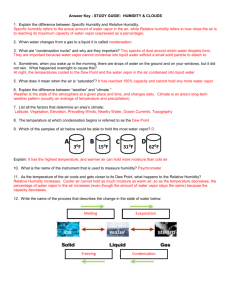
STUDY GUIDE: HUMIDITY & CLOUDS (WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE) 1. The actual amount of water vapor in the air is called Specific Humidity. The amount of water vapor in the air compared to the maximum amount of water vapor the air can hold is called Relative Humidity. 2. Are clouds made up of water vapor or liquid water? Liquid Water 3. What role does condensation nuclei have in cloud formation? Water vapor cannot condense into liquid water without something solid to attach onto so specks of dust or salt particles in the air allow water to condense around it to form cloud drops. 4. Give an example of something that could act as condensation nuclei: tiny specks of dust or salt in the air 5. Sometimes, when you wake up in the morning, there are drops of water on the ground and on your windows, but it did not rain. What happened overnight to cause this? The temperature dropped below the Dew Point and the water vapor in the air condensed into liquid water. 6. What does it mean when the air is “saturated”? It has reached 100% capacity & can’t hold any more water vapor. 7. Explain the difference between “weather” and “climate”. Weather is the state of the atmosphere at a given place and time, and changes daily. Climate is an area’s long-term weather patterns (usually in averages). 8. List all the factors that determine an area’s climate: Latitude, Vegetation, Elevation, Prevailing Winds, Nearby Water, Ocean Currents, Topography 9. The temperature at which the air is saturated with water is referred to as the Dew Point 10. Which of the volumes of air below would be able to hold the most water vapor? D. 3⁰F 15⁰F 31⁰F 62⁰F Explain. It has the highest temperature, and warmer air can hold more moisture than cold air. 11. What is the name of the instrument that is used to measure humidity? Psychrometer 12. As the temperature of the air cools and gets closer to its Dew Point, what happens to the Relative Humidity? It increases. Cooler air cannot hold as much moisture as warm air, so as the temperature decreases, the percentage of water vapor in the air increases (even though the amount of water vapor stays the same). 13. Write the name of the process that describes the change in the state of water below: Melting Evaporation Water Vapor Label each diagram below with the correct type of Precipitation (Sleet, Rain, Freezing Rain, and Snow): Freezing Condensation 14. Rain 15. Snow 16. Sleet 17. Freezing Rain Using the Dew Point/Relative Humidity tables (attached below), answer the following questions: 18. Dry-Bulb Temp. = 22⁰C, Wet-Bulb Temp. = 20⁰C. Dew Point temperature = 19°C 19. Dry-Bulb Temp. = -2⁰C, Wet-Bulb Temp. = -6⁰C. Dew Point temperature = -20°C 20. Dry-Bulb Temp. = 12⁰C, Wet-Bulb Temp. = 12⁰C. Dew Point temperature = 12°C 21. Dry-Bulb Temp. = 22⁰C, Wet-Bulb Temp. = 20⁰C. Relative Humidity = 83% 22. Dry-Bulb Temp. = 4⁰C, Wet-Bulb Temp. = -1⁰C. Relative Humidity = 27% 23. Dry-Bulb Temp. = 12⁰C, Wet-Bulb Temp. = 12⁰C. Relative Humidity = 100% Use the Cloud Base Graph to complete the following: 26. Air Temp. = 22⁰C, Dew Point = 20⁰C. Cloud Base Height = .25 km 27. Air Temp. = 6⁰C, Dew Point = 2⁰C. Cloud Base Height = .5 m 28. Air Temp. = 12⁰C, Dew Point = 12⁰C. Cloud Base Height = 0 km Fill in the blank with the word that best completes the sentence: 30. Clouds are classified by their shape and altitude. 31. Clouds that form in layers are called stratus. 32. High, feathery ice clouds are called cirrus. 33. Fluffy clouds with flat bases are called cumulus. 34. Dark rainclouds are called nimbostratus / cumulonimbus. 35. Clouds that produce lightning and tornados are called cumulonimbus. 36. All clouds form in the layer called the troposphere.