File
advertisement

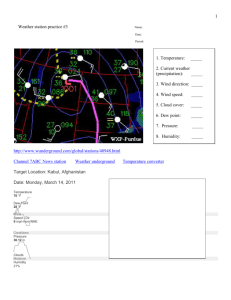
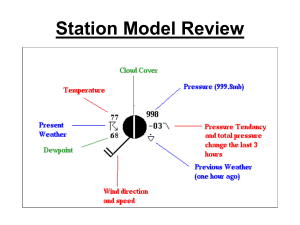
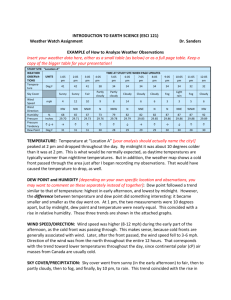
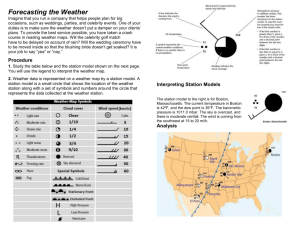
Climate and Meteorology 4 Meteorology Introduction: Collect hourly weather data for one day Make weather station models of the data. Graph weather data. Write analysis and reflection of the lab. Objective The objective of this lab assignment is to determine how we can use weather data to predict the weather. Problem How can we use the relationships among weather data to produce a forecast? Prediction What will the weather be like at the location of your choice> Why? Materials and Procedures Use the National Weather Service site to choose a location for your hourly observations. http://weather.noaa.gov/ All 24 hours are already recorded – you don’t have to do this yourself!! Weather.noaa.gov Now we choose a location – any location! This is what you should see now… Insert Table 8 columns, 24 rows Weather Data-Location: Titusville, Fl Date: September 7th and 8th Time Temp(F) Air Humidity Cloud Wind Dew Add’l Pressure Cover Speed and Point Weather Direction (F) Data 00:53 82 1013.5 77% None NE 5 mph 74 none What does the Sky Conditions column mean? CLR = clear FEW = partly cloudy SCTD= scattered clouds BKN= very cloudy OVC= overcast NA = no information available Why is it important to be able to predict the weather? Weather Station Models: You might not have 4 am and 4 pm exactly, use the time closest to them Be sure to do both!! Why would a weather station model be used instead of saying all the weather conditions? 82 F 74 F 1013.5 5 mph This is the part with the graphs! Part III: Creating Graphs (30 Points) Time on the X axis Temperature for the Y axis Include units and add titles to the graphs. Use www.chartgo.com Copy and paste the sharedURL in the space below. Example: http://www.chartgo.com/share.do?id=9611ba43aa Dew point Temperature and Air Temperature I know what air temperature is …dew point??? Dew point Temperature and Air Temperature Dew point is the temperature that the air is saturated with water vapor– think of humidity. High dew point temperatures – 70 and above – tend to be more humid, and can feel uncomfortable. If the dew point is high, there is a better chance there is fog, severe humidity, or even rain. When the air temperature is high, you sweat to cool down – if the dew point temperature is high, your sweat doesn’t evaporate, making you feel sticky and hot! Let’s make a graph! Under the chart is the link to paste into your lab report! Air Pressure Graph What do you think air pressure is? Air pressure in our lives We check air pressure in our tires – if it’s low, the tires go flat! When you go up in an airplane or climb a very tall mountain, air pressure decreases. WHY? When you go up in an airplane or climb a very tall mountain, air pressure decreases. WHY? There is less air. Zero air pressure creates a vacuum – think of outer space No air pressure is not pretty for people! Changes in air pressure causes the wind to blowWarm, low density air (low air pressure) rises, cool, higher density air sinks in to replace it. Wind speed and direction is predicted using air pressure Now create the Air Pressure Graph Chart title: Air Pressure X title: Time Y title: Air Pressure Analysis and Conclusions 1. In your own words, write an analysis of the weather that occurred on the day you selected, based on the surface weather station models you created. What was the weather like that day?? Reflection Questions:(12 points) 1. What did you learn about weather forecasting by completing the activity? 2. In your own words, how are weather data used to make forecasts? 3. In your own words, what is the relationship between temperature, dew point, and air pressure? Think about the graphs and what we discussed! 4. Did your findings support your weather predictions? What are the possible sources of error? (I read it wrong is not always a reason!)