MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
advertisement
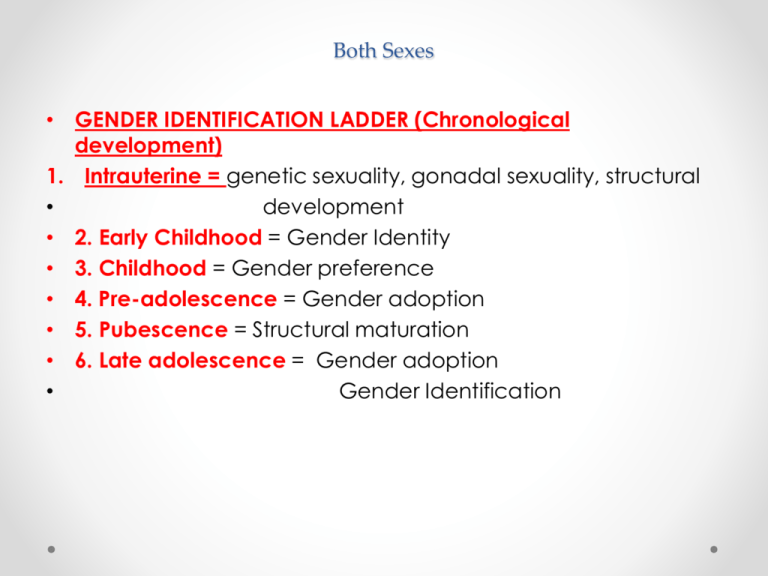
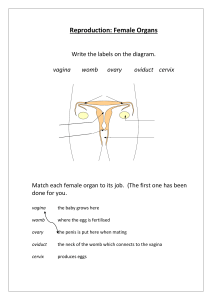
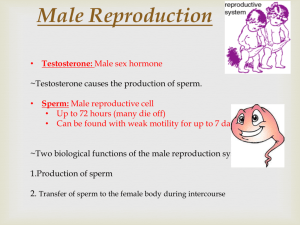
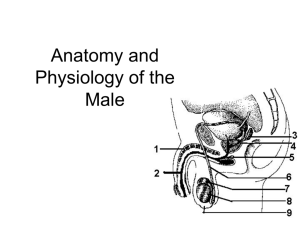
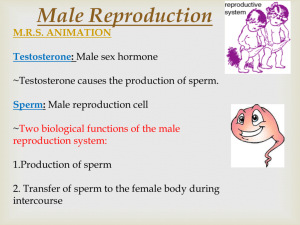
Both Sexes • GENDER IDENTIFICATION LADDER (Chronological development) 1. Intrauterine = genetic sexuality, gonadal sexuality, structural • development • 2. Early Childhood = Gender Identity • 3. Childhood = Gender preference • 4. Pre-adolescence = Gender adoption • 5. Pubescence = Structural maturation • 6. Late adolescence = Gender adoption • Gender Identification MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM • Sexuality – quality of being sexual; Male v Female • Masculinity • - behavioral expressions traditionally observed in males • - EXAMPLES • Learned Behaviors • - behaviors taught to individuals as they grow • - become beliefs GENDER IDENTIFICATION LADDER (Chronological development) 1. Intrauterine = genetic sexuality, gonadal sexuality, structural development 2. Early Childhood = Gender Identity 3. Childhood = Gender preference 4. Pre-adolescence = Gender adoption 5. Pubescence = Structural maturation 6. Late adolescence = Gender adoption Gender Identification MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM • • • • • • • • • • • • • Penis – (Glans Penis) Sex organ Erectile Tissue – 3 cylindrical chambers – 2 cavernous & 1 spongy body – during stimulation = vasocongestion takes place Foreskin – surrounds head of penis Corona – rim of the head – contains nerve endings Scrotum- sac holding testes – temp reg. Gonads – testicles – male sex glands – produce testosterone and sperm Seminiferous tubules – structures in testes were sex cell produced Epididymis – on back half of testes – stores sperm Urethra – tube that extends from bladder – joins w/ vas deferens Seminal Vesicle – releases clear, alkaline fluid – nourishes sperm w/ fructose – adds to mobility Prostate Gland – alkaline fluid – protects from acidic areas in urethra & vagina Vas Deferens- transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct Ejaculatory Duct – tube which connects vas deferens & seminal vesicle to the urethra MALE • Cowpers Gland –(bulbourethral gland) lubricates urethra w/ clear viscous mucus • Semen – ejaculated fluid - contains Sem V, Prostate, Cowper o • - - http://www.newhealthguide.org/What-Is-In-Semen.html Male Reproductive System SPERM • Acrosome – cap structure that covers the head – contains enzymes that help sperm locate and penetrate ova membrane • Head – contains genetic material from male – 23 chromosomes • Mitochondria – midpiece – helps supply energy – converts fructose from Sem. Ves • Tail - movement – • Avg. amount of sperm in each ejaculation? DISORDERS IN MALES DISORDER What it is… Symptoms.. Treatment Jock Itch Fungal Infection of groin; exposure to moisture & heat increase risk Itchy, red rash Over-the counter creams; keep area dry Cystitis (Bladder Infection) Inflammation of bladder – bacterial infection Swelling bladder, antibiotics burn when urinating, blood in urine, strong smell, fever Prostatitis Bacterial Infect. may be tied to STI Swelling, fever, pain in mid section & urinating antibiotics Inguinal Hernia Bulging of intestine through weakness of abdominal wall in scrotum Bulge in scrotum, sense of pain, heavy Immediate medical care surgery Disorder What it is Symptoms Treatment Testicular Torsion Twisting of testes on nerve/blood vessel attached to it Pain/nausea Immediate MX care – untwist or remove testes Prostate Cancer Abnormal cell growth Difficult to urinate, Surgery, Radiation burning & pain implant, chemo Testicular Cancer Cancer growth in testes – most common ages 1535 Lump on testes; heaviness in scrotum or no symptoms Self- exam monthly – chemo, surgery HEALTHY BEHAVIORS • • • • • • • • • Wear protective gear when playing sports Avoid wearing tight clothes Practice good hygiene Not circumcised, wash underneath foreskin Monthly TCSE Annual physical exam Moderate use of alcohol when of age Avoid smoking & drug use Exercise regularly – can prevent ED as you get older and help lessen chance of diabetes, cardiovascular disease & hypertension.