The Male Reproductive System
By: Assad Ab & Pedro Araujo
Functions of the Male Reproductive System
To Maintain, to transport, and to produce sperm
(the male reproductive cell).
To produce protective fluid (semen)
To ejaculate sperm within female reproductive tract
during sexual intercourse.
To produce and secret male sex hormones that are
responsible for maintaining the male reproductive
system.
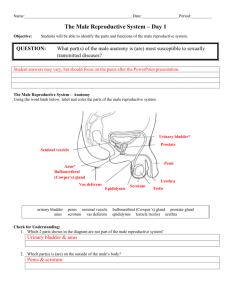
Diagram of the Male Reproductive System
Side angle view
Diagram of the Male Reproductive System
Front angle view
Structure & Functions
• Penis: This is the male organ used for
urination and sexual intercourse.
– Parts:
• Glans (head of the penis): Covered
with foreskin
• Corpus cavernous: Two columns of
tissues that are filled by blood and
causes an erection.
• Corpus Spongiosium: A column of
sponge like tissue, that fills with
blood during an erection, keeping the
urethra open.
• Scrotum: A loose pouch-like sac of skin
that hands behind the penis. It contains
the testicles as well as many nerves and
blood vessels.
– The scrotum has a protective function and acts
as a climate control system for the testes.
• Testicles (testes): They are oval shaped
organs that lie in the scrotum.
– They are responsible for making testosterone –
the primary male sex hormone.
– They generate sperm.
• Epididymis: A long and entwined tube that
lies on the backside of each testicle.
– Its functions are to transport and store the
sperm cells that are produced in the testes.
– The epididymis also is responsible for bringing
sperm into maturity, because the sperm emerging
from the testes are incapable of fertilization.
– After sperm has been brought to maturity, they
are transported to the vas deferens.
• Vas Deferens: A long muscular tube that
travels from the epididymis into the
pelvic cavity (just behind the bladder).
– It’s function is to transport mature/fertile
sperm to the urethra so that it is ejaculated.
• Seminal Vesicle: Are sacs that attach to
the vas deferens near the base of the
bladder.
– The produce fructose that provides sperm with a
source of energy and hence its mobility.
• Bladder: Is a muscular sac that keeps
urine until it is released into the
urethra.
• Prostate Gland: The prostate gland is part
of the male organ located in the lower
abdomen, below the bladder. The function
of the prostate is to produce seminal
fluid to dissolve the sperm produced by
the testes
How does the Male Reproductive System Function?
The entire male reproductive system is
dependent on hormones, which are chemicals
that regulate the activity of cells or
organs.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v
=T-rhWKZXaYw
- AWESOME VIDEO GUYS! XD
Bibliography
• http://men.webmd.com/picture-of-the-penis
• http://www.cchs.net/health/healthinfo/docs/2300/2376.asp
• http://www.webmd.com/sexrelationships/guide/male-reproductive-system