Reproductive System
advertisement

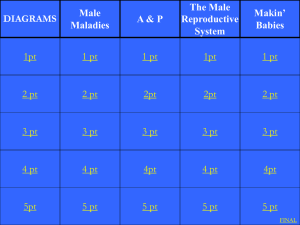
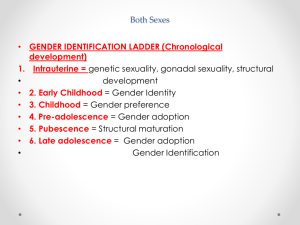
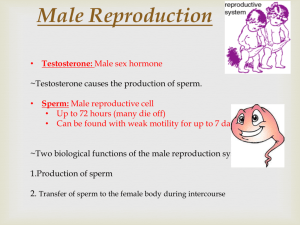
Name: __________________________ Class #: _______Class Period: __________ Date: _______________ Male Reproductive System Notes Sheet Anatomy of Male Reproductive System 1. Testes – male gonads located in the __________________ that produce sperm. a. Also produces male hormones, mainly __________________. i. ________________________ of sperm, body hair, facial hair, _____________ muscles, deep voice. 2. Scrotum – a ____________ suspended between the thighs. a. Temperature of the scrotum is _____________ than inside the body so that sperm can be produced. 3. Epididymis – a ___________________ coiled tube approximately 20 feet in length and located in the scrotum near the _____________________. a. After sperm develop in the _______________________ tubules in the testes, they enter the epididymis. b. Stores the sperm while they mature and become _______________ and produces a fluid that becomes part of semen. c. Then connects with the next tube, the ________ __________________. 4. Vas deferens - receives the _______________ and fluid from the _________________________. a. Joins with the epididymis and extends up behind the ____________________ bladder and joins with a seminal vesicle. b. Acts as both a _____________________ and storage area for sperm. c. This is cut during a ________________________________ to produce sterility in the male. 5. _____________________ vesicles – two small pouch-like tubes located behind the bladder a. The glandular lining produces a thick, yellow fluid that is rich in _________________ and other substances to provide __________________________ for the sperm. b. This composes a large part of the __________________. 6. Ejaculatory ducts – two __________________ tubes formed by the union of the vas deferens and the _______________________ vesicles. a. Carry the sperms and fluids (collectively known as semen) through the __________________ gland and into the ________________. 7. _________________________ gland – doughnut-shaped gland located below the urinary bladder on either side of the urethra. a. Produces an __________________ secretion that both increases sperm motility and neutralizes the acidity in the _______________________, providing a better environment for the sperm. b. Prostate contracts during ejaculation to aid in the _____________________ of semen. c. When it contracts, it also closes off the ____________________, preventing urination. 8. Cowper’s gland – two small glands located below the _____________________ and connected by small tubes to the urethra. a. Secrete ________________ and an alkaline fluid which decrease the acidity of _____________ residue in the urethra. Name: __________________________ Class #: _______Class Period: __________ Date: _______________ 9. Urethra – tube that __________________ from the urinary bladder, through the penis, and to the outside of the body a. Carries urine from the ____________________ and semen from the reproductive tubes. 10. Penis – the ________________ male reproductive organ that is located in front of the scrotum. a. Glans penis – enlarged structure at the ________________ ___________. b. Glans penis is covered with ________________ which is commonly removed during circumcision c. Functions include elimination of urine from the bladder as well as __________________ (penis fills with blood to become erect) Male Reproduction – Diseases and Abnormal Conditions 1. Epididymitis - ____________________ of the epididymis caused by a pathogenic organism a. Occurs with urinary tract or prostate infections, mumps, or ________________ b. If not treated, it can cause ________________ and ________________. c. Signs and Symptoms – pain in the testes, __________________, and fever d. Treatment – antibiotics, cold applications, scrotal support, and pain medication (draining of __________ or epididymectomy for severe cases) 2. ______________________ – inflammation of the testes a. Usually caused by the virus that causes ________________, bacterial infections from STDs, or injury b. Can lead to ________________ of testes and sterility c. Signs and Symptoms – _________________ of the scrotum, pain, and fever d. Treatment – antibiotics, ______________________, scrotal support, and pain medication e. Prevention – _____________________ and preventing STDs. 3. Prostatic hypertrophy – ___________________________ of the prostate gland a. Common in men over ________________ b. Can be __________________ or malignant c. Signs and Symptoms – difficulty starting to urinate, frequent urination, __________________, urinary infections d. Treatment – antibiotics, medications to shrink the ________________ size, medications to relax the urethra, removal of part of the prostate, or radiation and chemotherapy for prostate cancer 4. Testicular cancer – cancer of the ________________, occurs most frequently in men between 20-35 a. Highly _________________ form of cancer that can spread rapidly b. Signs and Symptoms – __________________ swelling of the testes, a heavy feeling, and an accumulation of fluid c. Treatment – ____________________, chemotherapy and/or radiation d. One of the most _________________ cancers with a 95% survival rate if it is detected early (__________________ testicular self-examinations).