Reproductive System Male Chapter 24
advertisement

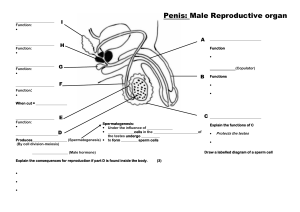
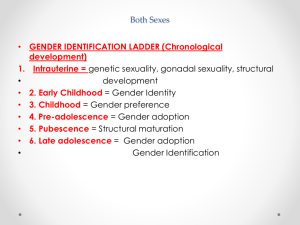
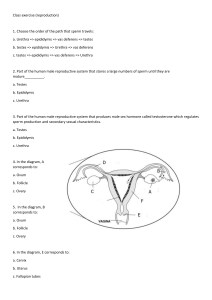
Reproductive System Male Chapter 24 Function • Gonads (testes and ovaries) – produce gametes (sperm and oocytes). • Gonads secrete hormones that regulate formation of sex cells and maintain gender specific sex characteristics. • Glands, external genitalia, and ducts are used in transporting and storing gametes. • Uterus supports the life of developing offspring until birth. Scrotum – sac that hangs from the root of the penis and consists of loose skin and superficial fascia. It supports the paired tests Dartos muscle – (smooth muscle), found in the vertical septum that divides the scrotum and continues into the subcutaneous tissue up to the abdominal wall. Dartos muscle – acts to regulate the temperature of the scrotum by contracting to wrinkle the scrotal skin which reduces the surface area available for heat loss. Temperature regulation is important for optimal spermatogenesis. Dartos muscle – Production and survival of sperm is dependent on a 3°C lower temp. than body temp. Cremaster muscle – covers the testes. Also aids in raising and lowering the testes. Continuous with the internal obliques. Testes – paired oval glands (4cm long, 3cm dia. on avg.). Each covered by a tough fibrous capsule. Develop in abdomen of fetus and descend about month 7. Seminiferous tubules – thin dividers of C.T. divide the testes into about 250 lobules, each containing 1-3 coiled tubules (70 cm). Tubules contain specialized stratified epithelium and spermatogenic cells. Interstitial cells (Leydig cells) – cells that are in spaces between seminiferous tubules. Responsible for secretion of testosterone. Testosterone is the most important androgen (stimulating male characteristic development) or male sex hormone. Cells undergo a reduction and maturation in a process called spermatogenesis. Cells ultimately released into lumen of seminiferous tubule. Approx. 300 million sperm are produced each day. Development cycle of sperm is approximately 60-75 days. Male Hormone Development 1. hypothalamus secretes gonadotropin releasing hormone (GRH) 2. stimulates pituitary to release leutenizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). 3. LH triggers leydig cells to produce testosterone 4. FSH stimulates spermatogenesis 5. Testosterone converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in some tissues, a potent androgen. hypothalamus GRH pituitary Androgen functions: LH FSH 1. stimulates male repro. organs before birth 2. further development, enlargement of male sex organs, and secondary masculine characteristics. leydig Cell T sertoli cell 3. aids in spermatogenesis and libido. 4. promotes aggressiveness and increase BMR. tissues spermatogenesis Epididymis – posterior border of testes. Storage of mature sperm occurs here up to one month. Vas deferens (ductus deferens) – widening of epididymis duct. Vas deferens It ascends the medial side of each teste, penetrates the inginual canal, enters the pelvic cavity, loops over the ureter, and posterior to the bladder, where it joins the ejaculatory duct located in the prostate gland. Seminal vesicle – A structure in the male that is about 5 centimeters (2 inches) long and is located behind the bladder and above the prostate gland. The seminal vesicles contribute fluid to the ejaculate. Fluid makes up about 60% of semen volume and contains acid neutralizers, sugars, coagulating enzyme and prostaglandans. Ejaculatory duct – formed by the union of the vas deferens and seminal vesicles. Prostate Gland – Inferior to bladder and surrounds urethra. Contributes about 25% of semen volume which contains proteolytic enzymes and citrate. Bulbourethral glands (Cowper’s gland) – paired glands inferior to prostate. Opens into spongy urethra. During sexual arousal it adds lubricant (mucous) to urethra. Penis – cylindrical organ that transports urine and semen to the external environment. Body of penis contains 3 cylindrical masses, each contains erectile tissue permeated by blood sinuses. Distal end of corpora cavernosa is enlarged into the structure glans penis, which contains sensory nerve endings associated w/ sexual pleasure. Covering of the glans in an uncircumcised penis is the prepuce (foreskin). Corpus spongiosum – single, smaller cylindrical mass that contains the spongy urethra. Vasectomy - a surgical procedure designed to make a man sterile by cutting or blocking both the right and left vas deferens, the tubes through which sperm pass into the ejaculate. Castration: Removal of the sex glands, usually used to indicate removal of the male testicles. Removes effects of testosterone.