Male Reproduction
advertisement

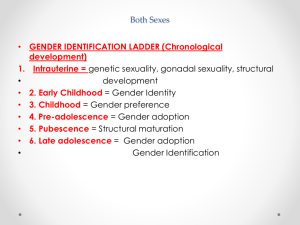
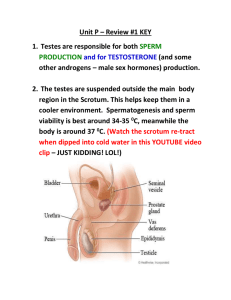
Male Reproduction • Testosterone: Male sex hormone ~Testosterone causes the production of sperm. • Sperm: Male reproductive cell • Up to 72 hours (many die off) • Can be found with weak motility for up to 7 days ~Two biological functions of the male reproduction system: 1.Production of sperm 2. Transfer of sperm to the female body during intercourse External Organs • Penis: Tube-like organ attached to the trunk of the body just above testes. • Functions: Sexual reproduction, sexual pleasure and elimination of waste. • Testes: male sex hormone/reproductive cell is produced here • Scrotum: Protects sperm by keeping the testes 3-4 degrees below normal body temperature. • Regulates the temperature of the testes • If the temp. rises, the muscles of the scrotum relax, lowering the testes. • If the temp. drops, muscles contract, pulling testes closer to the body. • Erectile Tissue: Tissue that becomes engorged with blood when a man becomes aroused Internal Organs • Epididymis: Stores newly produced sperm for about 64 days until fully matured. • Vas Deferens :A pair of connecting tubes, each 18 inches long that lead up into the males’ body toward other internal organs. • The duct that conveys sperm from the testicles to the urethra • Seminal Vesicles: Attached near the base of the bladder to the Vas Deferens. • The fluid contains nutrients and mixes w/ sperm. • Prostate Gland: Small gland that surrounds Urethra. • Secretes fluid that nourishes and protects sperm • Cowpers Gland: Two pea –sized glands that open into Urethra • Secretions from cowper’s glands help to protect sperm as it passes through the urethra • Pre-ejaculate clears any urine that may be present in the urethra • Urethra: Tube-like organ that travels through the penis, carries sperm and urine. • Semen and urine do not pass through the body at same time. • A muscle near the bladder contracts, preventing urine from entering urethra. • Ejaculation: Fluid from prostate, fluid from seminal vesicles and 300400 million sperm all combine to make semen • Semen: a thick fluid containing sperm and other secretions from prostate gland and seminal vesicles • Fertilization: Is the union of a reproduction cell from a male and one from a female. • Foreskin- penis is covered w/ a fold of skin at birth. • Circumcision: Surgical removal of the foreskin of the penis. Male Diagram Male Concerns • Hernia: Part of the body pushes through the muscle wall normally keeping it in. • (Example: Inguinal (In-gwin-al) Hernia- part of the intestine pushes through into scrotum. *Surgery is need to correct.) • Sterility: Sperm is weak, malformed, sparse or nonexistent. Fertilization does not occur. • Causes- Exposure to chemicals, smoking, STD’s, malfunction of one of the internal organs. • Prostate Cancer: Uncontrolled growth of cells. • Can only occur in males • Treatments- Removal of prostate or radiation therapy and hormonal therapy. • Testicular Cancer: Signs- Enlargement of testicles, lump or fluid collection, dull ache in the lower abdominal or groin area. • Frequently males 15-35. • Can only occur in males Preventing problems 1. Prevent STD’s 2. Prevent jock itch (fungal infection of the groin area) 3. Prevent Trauma (wear a sports cup) 4. Prevent hernias (caused by straining to push or lift something, heavy coughing or sneezing) 5. Prevent infertility 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Don’t smoke Limit alcohol consumption Steer clear of drugs Keep the weight off Reduce stress