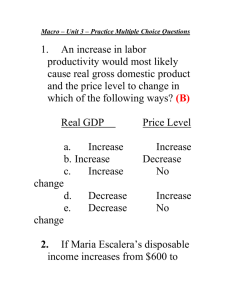
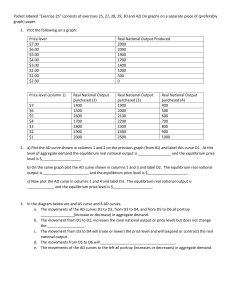
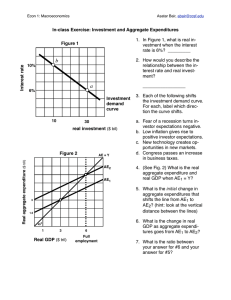
macro chap 8
advertisement
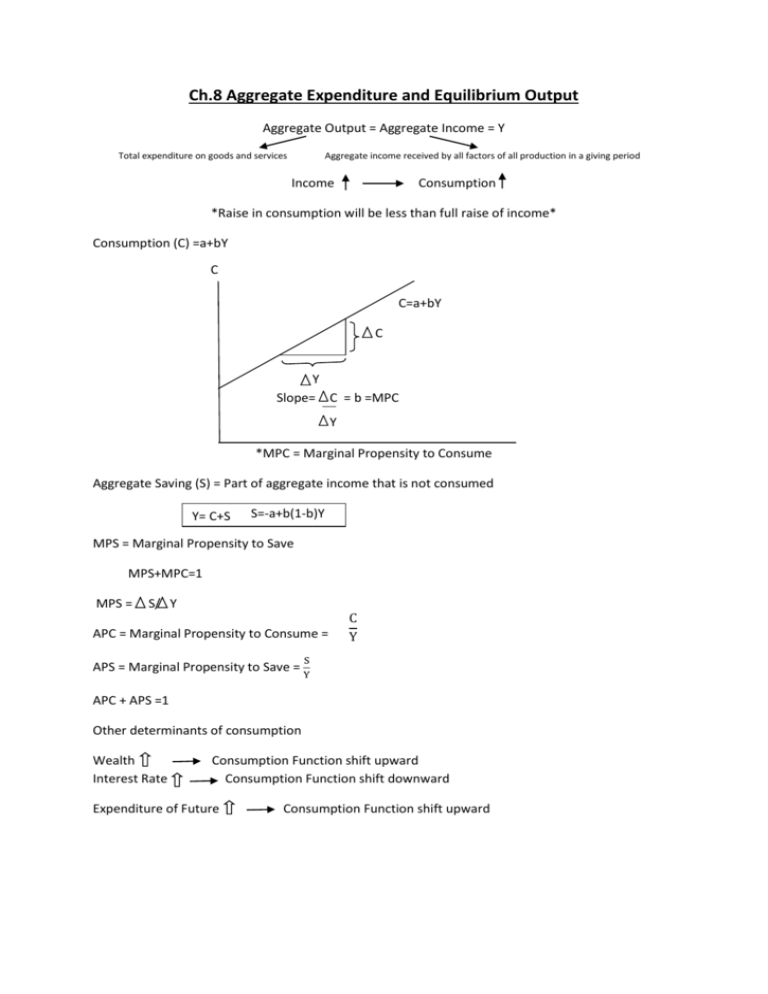
Ch.8 Aggregate Expenditure and Equilibrium Output Aggregate Output = Aggregate Income = Y Total expenditure on goods and services Aggregate income received by all factors of all production in a giving period Income Consumption *Raise in consumption will be less than full raise of income* Consumption (C) =a+bY C C=a+bY C Y Slope= C = b =MPC Y *MPC = Marginal Propensity to Consume Aggregate Saving (S) = Part of aggregate income that is not consumed Y= C+S S=-a+b(1-b)Y MPS = Marginal Propensity to Save MPS+MPC=1 MPS = S/ Y APC = Marginal Propensity to Consume = C Y S APS = Marginal Propensity to Save = Y APC + APS =1 Other determinants of consumption Wealth Interest Rate Consumption Function shift upward Consumption Function shift downward Expenditure of Future Consumption Function shift upward Planned Investment (I)= Investment that firm plan to make: assume that I is fix I Actual Investment= Planed Investment+ Unplanned Change in Investment Planned Aggregate Expenditure (AE) =Consumption + Planned Investment Y=AE Y=C+I Increase in Planed Investment (I) I product hire labor hire labor income income consumption consumption Multiplier 1 1 Planned Investment Multiplier (M) = 𝑀𝑃𝑆 =1−𝑀𝑃𝐶 demand for output firm Ch.9 Government and Fiscal Policy (add T and G) Government (G) Net Tax (T) 𝐺 > 𝑇 =budget deficit 𝐺 < 𝑇 = budget surplus Disposable income (Yd) = Y-T Yd = C+S Y = C+S+T AE = C+I+G S+T = I+G C = a+b(Y-T) S = -a+(1-b)(Y-T) 1 1 Government Spending Multiplier (M) =𝑀𝑃𝑆 =1−𝑀𝑃𝐶 ∆ Equilibrium GDP (∆Y)= ∆Govt. Spending × Government Spending Multiplier (M) Tax Multiplier = −𝑀𝑃𝐶 𝑀𝑃𝑆 ∆ Equilibrium GDP (∆Y)= ∆𝑇𝑎𝑥 × Tax Multiplier Closed Economy AE = C+I+G Y = AE C+S+T = C+I+G S+T =I+G G >T Govt. budget deficit G <T Govt. budget surplus G =T Govt. budget balance Opened Economy AE = C+I+G+(EX+IM) Y = AE C+S+T = C+I+G+(EX+IM) S+T =I+G+X Two types of policy 1. Expansionary Fiscal Policy Decrease Tax and Increase Govt. Spending 2. Contractionary Fiscal Policy Increase Tax and Decrease Govt. Spending