FOR AVERAGE STUDENTS Part – B MACRO ECONOMICS
advertisement

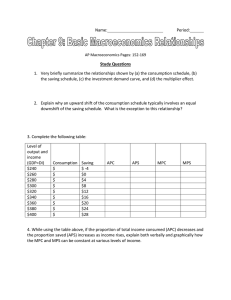
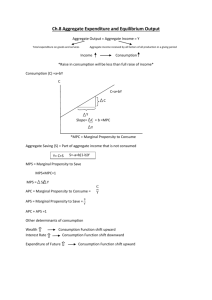
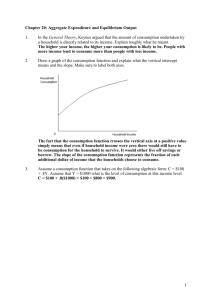
FOR AVERAGE STUDENTS Part – B MACRO ECONOMICS UNIT VI: NATIONAL INCOEM AND RELATED AGGREGATES ( 15 MARKS) (one mark question) 1. Is the study of cotton textile industry a macro economic study or micro economic study? 2. Two main problems studied in Macroeconomics. 3. Define Macroeconomics. 4. Two examples of macro economic variables. 5. Define consumer goods. 6. What are producer goods? 7. What are capital goods? 8. Basic difference between final and intermediate goods. 9. Define stock and flow. 10. What is consumption of fixed capital or deprecation. 11. state, which of the following is a stock or a flow a. wealth b. cement production 12. What is investment? 13. If an economy investment is greater than saving, what is the effect on the national income. 14. What are transfer payments? 15. Define forced transfer. 16. what is real national income 17. if domestic income is Rs. 500 cr and net factor income from abroad is Rs. (-5) cr. How much will be national income. 18. when will be domestic factor income greater than national income 19. Meaning of non-market activities. 20. Which of the following is not included in national income? i) Old age pension. ii) Purchase of a new car. 21. What is a GNP deflator? 22. Define the concept of value added. 23. Define nominal GDP 24. Define real GDP 25. Is net of exports (x-m) a part of net factor income from abroad ? (3/4 marks questions) 1. Describe the important features of a capitalist economy. 2. Describe the great recession of 1929. 3. What are the 4 factors of production and what are the remunerations to each of these called ? 4. Differentiate between planned and unplanned inventory accumulation. 5. What is difference between budget deficit and trade deficit ? 6. Suppose the GDP at market price of a counting in a particular year was Rs. 100 Cr., Net factor income from abroad was Rs. 100 cr ,the value of indirect taxes subsidies was Rs. 150 Cr. and national income was Rs. 850/- cr. Calculate the aggregate value of depreciation. 7. Differentiate between monetary flow and real flow. 8. What is meant by circular flow of income? Name its 3 related phases. 9. Explain the concept of leakages and injections in the circular flow of income. 10. Differentiate between private income and personal income. 11. What is difference between factor inputs and non- factor inputs ? 12. Show as how the sum of value added is equal to sum of factor income ? 13. State any 4 precautions while measuring national income by income method. 14. Find out personal disposable income. Corporation tax Misc receipts of Govt. Direct taxes paid by household Saving of private corporate sector Net of retained earnings of foreign companies Private income 15. Find out private income from the following i) Corporation tax ii) Direct taxes paid by households iii) Personal disposable income iv) Misc. receipts of govt. administrative v) Saving of private corporate sector net of retained earnings of foreign companies. 3 cr. 1 cr. 4 cr. 1cr 218 cr. 4cr. 6cr 317 cr. 02 cr. 02 cr. 16. Calculate NDP at MP from the following. i) Net indirect taxes 38 cr. ii) Consumption. Of fixed cap. 34 cr. iii) Net factor income from aboard (-)3 cr. iv) Rent 10 cr v) Profit 25 cr. vi) Interest 20 cr. vii) Royalty 5 cr. viii) Wages and salaries 170 cr. ix) Employers contribution to social security schemes 30cr 17. Calculate value added by firm x and firm y i) Sales by firm x to households ii) Sales by firm y iii) Purchases by households from firm y iv) Exports by firms y v) Change in stock of firm x vi) Change in stock of firm y vii) Imports by firm x viii) Sales by firm Z to firm y ix) Purchases by firm y from firm x 100 500 300 50 20 10 70 250 200 18. Calculate gross value added of factor cost. Sales 180 Rent 05 Subsidies 10 Change in stock 15 Purchase of raw materials 100 Profits 25 19. State the circular flow of monetary and real flow among 3 sector models of the economy. ( 06 Marks questions) 1. Explain the circular flow with 4 sector economy. 2. Will the following be a part of domestic factor income of India? Give reasons for your answer. i) Old age pension given by govt. ii) Factor income from abroad. iii) Salaries to Indian residents working in Russian embassy in India. iv) Profit earned by a company in India, which is owned by a non – resident. 3. Explain the problem of double counting in estimation of national income by giving suitable examples and 2 ways of avoiding this problem. 4. GDP may not be an appropriate index of welfare of the people. How? 5. From the following data, calculate NNP at Market price by i) Expenditure method ii) Income method. 1) Personal consumption exp. 700 2) Wages and salaries 700 3) Employers contribution to social security 100 4) Gross business fixed 60 5) Gross residential construction investment 60 6) Gross Public investment 40 7) Inventory investment 20 8) Profit. 100 9) Govt. Purchases of goods and services 200 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) 17) 18 Rent Exports Imports Interest Mixed income of self employed Net factor income from abroad Depreciation Indirect Tax subsidies 50 40 20 40 20 (-)10 0 20 10 6. Calculate (a) Personal Disposable income (b) National Income 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) Private income Mixed Income NFIFA Compensation of employees Net retained earnings of private enterprises Profit Rent Corporation Tax Interest Net Indirect Taxes Net exports Direct Taxes paid by households Consumption of fixed capital 4000 1200 -50 1300 200 800 600 400 700 500 -100 150 180 FOR AVERAGE STUDENTS Part – B MACRO ECONOMICS UNIT – 08 DETERMINATION OF INCOME AND EMPLOPMENT ( 12 Marks) One mark questions 1. Define aggregate demand. 2. What do you mean by aggregate supply? 3. What is effective demand? 4. What is paradox of thrift? 5. What do you mean by marginal propensity to consume? 6. What is marginal propensity to save? 7. If MPS is .5, what will be the value of multiplier? 8. If MPC is .8, what is the value of MPS? 9. Can the value of MPC be equal of one? 10. Define Marginal efficiency of capital. 11. What is consumption function? 12. What is the saving function? 13. What is autonomous consumption? 14. What can be the maximum value of marginal propensity to save? 15. Define multiplier. 16. What is excess demand? 17. What is deficient demand? 18. When does a situation of deficient demand arise in an economy? 19. Find out the value of multiplier when MPS = 0 20. What does MPC refer to in a diagram showing consumption function or consumption line? 21. What happens to an economy, if AD>AS. (3 / 4 marks question) 01. Find saving function when consumption function is given c = 1000 + .6y 02. Show diagrammatically, the effect on equilibrium. Level of output of govt. spending. 03. What happens if AD>AS prior to full equilibrium. Level of output. 04. Does an excess of AD over AS always imply a situation of inflationary 05. Complete the following. Income consumption MPC APC 1 12 20 26 gap? 40 60 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 40 54 An increase in investment by Rs. 400 cr. leads to increase in national income by Rs. 1600 cr. Calculate MPC In an economy, the marginal propensity to consume is 0.75 Investment is increased by Rs. 200 cr. Calculate the total increase in income and consumption expenditure. i) If the value of multiplier is 4, what will be MPC and MPS ? i) What increase in investment is needed to raise income to Rs 2000 cr. if MPS = 0.5. Explain any 3 measures by which excess demand in an economy can be corrected. Explain the concept of deflationary gap. Explain any two measures by which a central bank can attempt to reduce this gap. What is monetary policy? Explain the role of i) Bank rate and ii) Margin requirements in influencing the availability of credit in an economy. What is inflationary gat? What is its impact on output and prices? What is meant by ‘investment multiplier’? Explain the relationship between marginal propensity to consume and investment multiplier. Explain the working of investment multiplier with the help of a numerical example. What is the difference between planned investment and realized (actual) investment? (06 marks questions) 01. Measure the level of ex-ante aggregate demand when autonomous investment and consummation exp. (a) is Rs. 50 cr and MPS is 0.2 and level of income (y) is Rs. 4000/state whether the economy is in equilibrium. or not. Give reasons. 02. Given below is the consumption function in an economy c = 100+.05 y With the help of a numerical example show that in this economy, as income increases, APC will decrease. 3. 4. 5. 6. Calculate i) its equilibrium. Level of national income ii) saving at equilibrium. Level of national income when following information about an economy is given : Consumption function c= 200 + 0.9 y Investment expenditure = 3000 Give the meaning of excess demand in macro economics. Explain any 4 measure in monetary policy to correct it. Explain the concept of under employment equilibrium. With the help of a diagram, show the additional investment exp. required to reach full employment equilibrium. Explain the working of investment multiplier with the help of a numerical 7. 8. 9. 10. example. Draw a diagram a straight line saving curve for an economy. From it, derive the consumption curve explaining the method of derivation. Show a point on the consumption curve at which APS is equal to one. Explain the equilibrium level of income with the help of saving and investment curves. If savings exceeds planned investment what changes will bring about equality between them ? Explain the theory of determination of income and employment with the help of AD and AS curves and saving and investment approach. Differentiate between full employment and under employment equilibrium. with the help of a diagram.