1 ECONOMICS II EXTRA True or False CHAPTER 11
advertisement

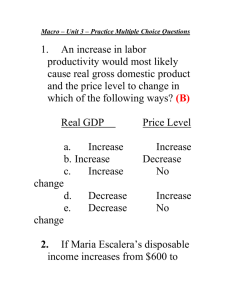
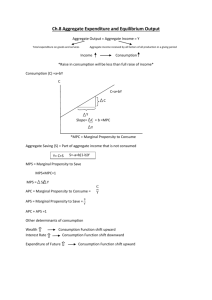
ECONOMICS II EXTRA True or False CHAPTER 11 (CLASSROOM PRACTICE) ANSWERS 1 Crowding out is more likely to occur when aggregate supply is perfectly elastic. A) True B) False Crowding is more likely to occur when aggregate supply is perfectly inelastic. An increase in government spending will raise prices while GDP remains constant. Therefore, the increase in spending by the government must directly crowd out private sector spending. 2 Investment is an autonomous expenditure A) True Investment decisions taken now are not influenced by the current level of income. B) 3 False The Keynesian explains the behaviour of inflation A) True B) False Under the Keynesian Cross approach there is an assumption that prices are constant. 4 The marginal propensity to consume is the level of consumption when income is zero. A) True B) False The MPC (marginal propensity to consume) is the extra consumption generated by 1 unit of extra income. 5 The marginal propensity to consume can never be equal to the marginal propensity to save. A) True B) False They can both be equal to 0.5 6 Adding investment to the AD curve does not change its slope A) True Adding investment to consumption simply increases autonomous expenditure by the increased amount of investment. B) False 7 In equilibrium, national output and aggregate demand must be equal. A) True For the Keynesian cross approach to modelling equilibrium output, see Figure 11.5 B) 8 False An increase in the marginal propensity to save increases the multiplier. A) True B) False It reduces the multiplier because the multiplier is equal to 1/(1-MPC)=1/MPS. 1 9 An increase in the tax rate reduces the multiplier. A) True Multiplier = 1/(MPS + MPT), where MPT is the marginal propensity to tax. B) 10 False Cumulative government debt is larger in Germany than in the UK A) True See Figure 11.9. B) False 2