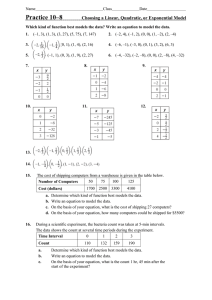
1.01 NeedsFor ITM
advertisement

http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zLYECIjmnQs Winners or losers? A series of activities that creates an exchange and satisfies the individual customer across national borders ◦ ◦ ◦ Identify customer needs Planning to meet those customer needs More complicated than domestic marketing: Cultural differences Political/legal differences Geographic differences Competitive differences ◦ Import/export ◦ Simplest and least risky strategy Contracting ◦ Contractual agreement to work with a foreign business partner Licensing agreements ◦ An agreement giving foreign companies the right to sell a company’s product for a fee Joint ventures ◦ Two or more businesses combine to create a new business Direct investment Purchasing business assets to run a business in a foreign country Advanced technology Improved transportation New market opportunities Advanced technology ◦ ◦ ◦ Internet connects customers and businesses worldwide Same movies, television shows, and Internet content are seen everywhere Companies can use the same media to send messages around the globe Improved transportation systems ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Faster and cheaper than in the past Sealed containers available for ocean shipping Satellite technology to avoid bad weather Numerous world-wide shipping companies (for example, UPS, FedEx) New market opportunities ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Fall of iron curtain in 1989 opened eastern Europe Opening of trade in China—largest market on earth Economic development in South America, Africa, Southeast Asia Increased personal income world-side Increased risk increases the need for an international marketing plan Must create and deliver value to differing customers Manage customer relationships Create a profit Understand how marketing activities differ in different cultural and political/legal environments Careers are diverse--some require a college degree, some only high school Ability to communicate in a foreign language is helpful Should develop a cultural understanding of the country where you will work Global businesses require more technology skills Experiences traveling, studying, or living abroad are helpful Involved in every transfer of goods and services to the consumer Distribution Pricing Promotion Financing Marketing-information management Product-service management Selling Distribution ◦ ◦ Determining the best ways to allow customers to locate and obtain the products & services of a business Involves shipping, handling, and storing of products Marketing-information management Obtaining, managing, and using marketing information to improve business decision-making Marketing research Developing databases of product, customer, and competitive information Pricing ◦ ◦ ◦ Establishing a price for goods and services Should set prices low enough to encourage customer purchase, and high enough to make a profit Manage international currency exchange rates Product/service management ◦ ◦ Designing, developing, maintaining, improving, and acquiring products to meet consumer needs and wants Producers and manufacturers develop products Promotion ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Communicating to potential customers about products and services Advertising Publicity/public relations Sales promotion Personal selling Selling ◦ ◦ ◦ Communicating directly with prospective customers to assess and satisfy needs Two-way interaction with customer May be face-to-face, via telephone, or Internet tools Financing ◦ ◦ ◦ Budgeting for marketing activities Obtaining funds for business operations Developing payment and credit systems to help customers purchase goods and services