3-20-13 Plant Structure FILL IN THE BLANK NOTES
advertisement

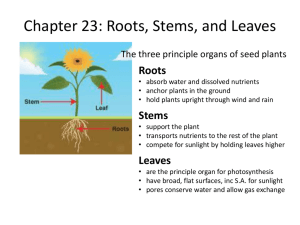
Plant Structure Notes Evolution and types of plants Since the earth was once covered in water, plants had to make survive on land The ability to The ability to The ability to adaptations to Plants can be placed under two groups - having true roots, leaves, and stems Ex. ferns, conifers, flowering plants - not having true roots, leaves, and stems Ex. mosses, liverworts, hornworts Vascular Plants can be divided into two groups Plants-Made up of ferns and plants closely associated with ferns Plants-Two types of seed plants 1. in fruit -which includes pine trees, produce seeds that are not encased 2. - aka flowering plants, produce seeds within a protective fruit The two main groups of angiosperms are the monocots and the dicots Monocots – _________________ cotyledon – ______________________ leaf venation – _________________________ vascular bundles – Flower parts in ___________________________________________ – _____________________________________ roots Dicots- aka eudicots – ________________________ cotyledons – ____________________________ leaf venation – __________________________________________of vascular bundles – Flower parts in ______________________________________________ – _____________________________________ system A typical plant body contains three basic organs: roots, stems, and leaves Plants water and minerals from soil through Plants the sun’s energy and carbon dioxide from the air through Plant roots depend on shoots for produced via photosynthesis Plant shoots depend on roots for and Plant roots – Anchor plant – Absorb water and nutrients – Store food Plant shoots – Stems, leaves, and reproductive structures – Stems provide support – Leaves carry out photosynthesis Many plants have modified roots, stems, and leaves Modifications of plant parts are adaptations for various functions – Food or water – reproduction – – – Root modifications – Food storage – Stem modifications – Runners (allow for asexual reproduction) Leaf modifications – – Examples include carrots & potatoes Climbing – tendril – Example: pea plants Protection – Thorns or spines – Example: Cactus spine Plants cells have three structures that distinguish them from animals cells – used in photosynthesis – A large, fluid-filled – A composed of cellulose PLANT GROWTH Plants are categorized based on how long they live – complete their life cycle in one year – complete their life cycle in two years – live for many years Primary growth vs Secondary Growth – Primary growth is the _________________________ of a plant (shoot ____________________ ____________ and root ______________________________________________). – Secondary growth is an increase in diameter of roots and shoots (________________________). – This growth does not occur at all parts of the body like in animals. This is because not all cells in a plant _____________________. – _______________________________________ – small, unspecialized cells that divide continually Meristem There are two types of meristem cells. 1. Apical meristem – located at the tips of roots and shoots Responsible for primary growth 2. Lateral meristem – cells responsible for creating more xylem / phloem and bark Responsible for secondary growth Secondary growth increases the girth of woody plants Vascular cambium produces the _________________________________________ Cork cambium produces the outer Wood annual rings show when new growth starts each year. (transport)- functional, lighter-colored wood near the outside of the trunk (storage)- the darker wood at the center of the trunk - transports water - transports food