Unit 2.03 PowerPoint & Notes
advertisement

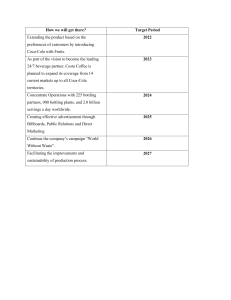
Principles of Business Finance and Marketing Unit 2 – Business in the Global Economy Section 2.03 – International Business Organizations NOTES MULTINATIONAL CORPORATION An organization that does business in several countries o Home country – the country where parent company o Host country – the country in which the MNC places is located business activities Global Top 100 Leading Industries 1. industrials 2. technology 3. financials Leading Countries 1. USA 2. United Kingdom 3. China Leading Companies 1. apple 2. exxon Mobil Corp 3. google Inc Global Strategy Uses the same Example: Coca-Cola 1886 1899 1909 1920s 1930s 1940s 1950s 1960s 1970-80s 1990s Today product and marketing strategy worldwide Coca-Cola invented as fountain drink/tonic began bottling nearly 400 bottling plants in operation bottled sales exceed fountain sales global expansion begins 64 bottling plants around world (supplying WWII soldiers) packaging innovations new brands introduced (Fanta, Tab, Sprite) consolidation to serve customers technology leads to a global economy international mega-chains new & growing markets previously closed, now open (eastern Europe, Africa) Coca-Cola is sold in more than 200 countries and is the most recognized brand in the world Multinational Strategy treats each country market differently Example: List 3 different McDonald’s menu items found around the world and where they’re from: Multinational Corporations Benefits large amount of goods available Lower prices Career opportunities Foster understanding, communication, and respect Friendly international relations Drawbacks Economic power Worker dependence on the MNC Consumer dependence political power GLOBAL MARKET ENTRY MODES Licensing Selling the right to use some intangible property (production process, trademark, or brand name) for a fee or royalty o Allows companies to produce items in other countries without being actively involved o Has a low company is often low The risk Example: o o financial investment, so the potential financial return for the for the company is low Franchising Right to use a company name or business process in a specific way o o o Allows organizations to enter into contracts with people in other countries to set up a business that looks and runs like the parent company Marketing elements, such as food products, packaging, and advertising, must meet both cultural sensitivities and legal requirements Commonly involves selling a product or service Joint Venture An agreement between two or more companies to share a business project o o o Allows two or more companies to share raw materials, shipping facilities, management activities, or production activities Concerns include the sharing of profits and not as much control because several companies are involved Very popular for manufacturing , such as Japanese and U.S. automobile manufacturers INTERNATIONAL TRADE ORGANIZATIONS World Trade Organization (WTO) Created in 1995 to promote trade around the world o 150 member countries o Settles trade disputes o Enforces free-trade agreements o Other goals Lowering tariffs that discourage free trade Eliminating import quotas Reducing barriers for banks, insurance companies, and other financial services Assisting poor countries with economic growth International Monetary Fund (IMF) Established in 1946 to help promote economic cooperation o Maintains an orderly system of world trade and exchange rates o Includes more than 150 member nations World Bank Created in 1944 to provide loans for rebuilding after WW II o AKA the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development o Today the World Bank has more than 180 member countries and two main divisions International Development Association (IDA), which makes loans to help developing countries International Finance Corporation (IFC), which provides technical capital and technical help to private businesses in nations with limited resources