Neurologic Assessment
advertisement

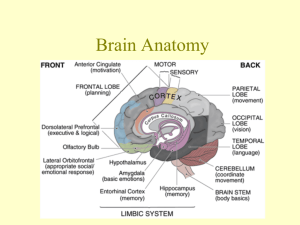
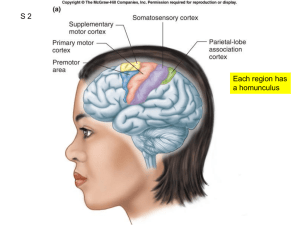
Denise Coffey MSN, RN Central Nervous System (CNS) Cerebral cortex Hypothalamus Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Occipital lobe Wernicke’s area Broca’s area Basal ganglia Thalamus Cerebellum Brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla Spinal cord Slide 23-2 Pathways of the CNS Crossed representation Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinothalamic tract Posterior (dorsal) column Corticospinal or pyramidal tract Extrapyramidal tracts Cerebellar system Upper motor neurons Lower motor neurons Slide 23-3 Slide 23-4 [PRODUCTION NOTE: Please insert Figure 23-2 (from Jarvis Physical Examination and Health Assessment, 5e, ISBN: 978-1-4160-3243-4)] © Pat Thomas, 2006. Slide 23-5 © Pat Thomas, 2006. Slide 23-6 Headache Head injury Dizziness/vertigo Seizures Tremors Weakness Slide 23-7 Preparation Screening neurologic examination Complete neurologic examination Neurologic recheck Equipment needed Penlight Tongue blade Cotton swab Cotton ball Tuning fork (128 or 256 Hz) Percussion hammer Occasionally need: familiar aromatic substance Slide 23-8 Test Cranial Nerves I—Olfactory II—Optic III—Oculomotor, IV—Trochlear, VI—Abducens V—Trigeminal Motor function Sensory function Corneal reflex VII—Facial Motor function Sensory function VIII—Acoustic (vestibulocochlear) IX—Glossopharyngeal, X—Vagus Motor function Sensory function XI—Spinal accessory XII—Hypoglossal Slide 23-9 Motor System—Inspect and palpate Muscles Cerebellar function Size Strength Tone Involuntary movements Balance tests Gait Tandem walking Romberg’s test Shallow knee bend Rapid alternating movements Finger-to-finger test Finger-to-nose test Heel-to-shin test Coordination and skilled movements Slide 23-11 Sensory System Person is alert, cooperative, and comfortable Guidelines for sensory testing Spinothalamic tract Pain Temperature Light touch Posterior column tract Vibration Position (kinesthesia) Tactile discrimination (fine touch) Stereognosis Graphesthesia Two-point discrimination Extinction Point location Slide 23-12 Test the stretch or deep tendon reflexes Technique Grading Reinforcement Biceps reflex Triceps reflex Brachioradialis reflex Quadriceps reflex Achilles reflex (“ankle jerk”) Test the superficial reflexes Abdominal reflex Cremasteric reflex Plantar reflex Clonus Slide 23-13 Neurologic recheck Level of consciousness Person Place Time Motor function Pupillary response Vital signs Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) Slide 23-14 Oculomotor response (Cranial nerve III) Size, equality, and roundness of pupils assessed Size measured in millimeters Evaluated for symmetry in size and response to light stimulus Brisk, sluggish, non-reactive Consensual reaction of opposite pupil at same time Assess accommodation by holding finger 4-6 inches from client’s nose and then pull out to 18 inches. As finger moves away pupil will accommodate by dilating, as finger moves closer, constricting PEARLA- Pupils equal and reactive to light and accommodation Ability to follow commands Muscle tone Muscle strength Coordination Balance (Romberg test) Posturing (Decorticate, Decerebrate) Tactile sensation Pain Temperature Vibratory sensation Tactile discrimination Superficial Deep tendon Biceps Triceps Patellar Achilles Plantar (Babinski Response) Clear and appropriate Confused Inappropriate Garbled Aphasia (Expressive, Receptive) Limited hearing Use of hearing aids Slide 23-26 Slide 23-27 Slide 23-28