motorcontrol
advertisement

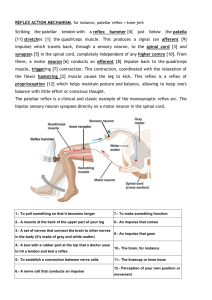
S2 Fig. 10.10a Each region has a homunculus Decision to move S4 Fig. 10.01 Initiates motor command Coordinates secondary movements Corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts Balance and complex learned movements Pathways? Other inputs: Vestibular & Visual! Reflex Examples of motor disorders: Huntington’s Disease and Cerebellar Disorder S5 Jack Nicholson One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest Frontal lobotomy S 16 Pyramidal tract Fig. 10.12 Corticospinal tract Corticobulbar tract Fine motor control, esp. of extremeties Extra-Pyramidal tracts Reticulospinal tract Vestibulospinal tract Originate in brainstem, more involved with posture and equilibrium Diagram is not accurate: This is not a monosynaptic pathway! Descending axons synapse onto interneurons which then synapse onto motoneurons. Descending Pathways S 17 Who Cares? Video of Huntington’s Chorea Video of Cerebellar Dysfunction Locked-in Syndrome S6 Local control • Muscle spindle Spindle Afferent gamma motoneurons – Stretch receptor – Intrafusal muscle fiber • What is their role? • The stretch reflex… – Follow the reflex arc – Be able to differentiate function of afferent fibers, alpha motor neurons, and gamma motor neurons Motor units of alpha motoneurons S7 Fig. 10.05ab This doesn’t happen! S8 Fig. 10.05c Co-activation of alpha and gamma motoneurons insures that the stretch of muscle can be detected regardless of the initial length or state of contraction of that muscle. S9 Fig. 10.06 Proprioception pathway via dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway One component of Stretch reflex is monosynaptic Most common example: patellar reflex = “knee jerk reflex” Synergistic & Antagonistic Muscles S 10 Stretch Reflex Monosynpatic excitation of motoneurons of that muscle and synergistic muscles and polysynaptic inhibition of motoneurons to antagonistic muscles. Recall frog reflex lab and existence of spinal reflexes in single-pithed frogs. Also, example Christopher Reeve and patellar reflex. S 11 Fig. 10.07 S 12 Golgi tendon organs involved in a reflex to oppose excessive muscle tension. Not monosynaptic. Not shown in text diagram: ascending axons in dorsal column-medial lemniscus tract. S 13 Other proprioceptors Joint angle detectors and cutaneous mechanoreceptors also contribute to sense of body position (proproiception.) Plus vision and vestibular inputs! S 15 Something is incorrect on this figure from another textbook. Find it!