CNS-3
advertisement

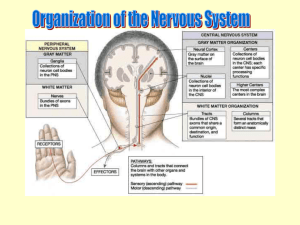
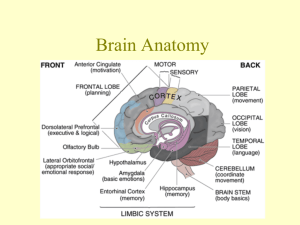
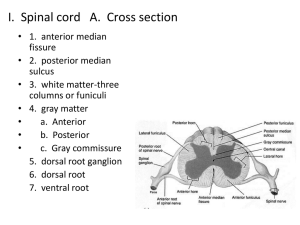
Part 6 The Sensory Function of CNS Sensation production Changes of internal and external environment Interoceptor and exteroceptor Sensation conduction pathway Thalamus and cerebral cortex Superficial sensation Corresponding reflex Senses Somatic senses Mechanoreceptive Tactile and position Thermoreceptive Pain sense Special somatic senses senses senses Five basic types of sensory receptors Mechanoreceptors Thermoreceptors Nociceptors (Pain receptors) Electromagnetic receptors Chemoreceptors The somatosensory system includes multiple types of sensation from the body--- light touch, pain, pressure, temperature, joint and muscle position sense (also called proprioception). Sensory pathways: Spinal cordBrainstem Thalamus Cerebral cortex Spinal cord Sensory pathways in spinal cord Two alternative pathways: The Fine touch, two-point discrimination, phasic or position sensation dorsal column cross in medulla medial lemniscal system thalamus The dorsal column-medial lemniscal system anterolateral system Pain, warmth, cold, crude tactile, tickle and itch, sexual sensation dorsal spinal roots cross in spinal cord brain stem and thalamus 1.The dorsal column-medial lemniscal system 2. The anterolateral system Structure of Thalamus Function of thalamus A relay station to the cerebrum for all varieties of sensory input except olfaction 1. Specific sensory relay nuclei Somatosensoryventral-posterior (VP thalamus) somatosensory area I Visual signal lateral geniculate body visual cortex Auditory signal medial geniculate body auditory cortex Nuclei of Thalamus 2. Associated nuclei Association nuclei receive their driving inputs from other cortical areas Anterior nucleus ventral-lateral nucleus Pulvinar nucleus 3. Nonspecific projection nuclei “Nonspecific nuclei" connect to association areas of cortex Medial nucleus Nuclei in lamina Specific projection system of thalamus The projecting system of thalamic relay nuclei receives fibers from ascending somatosensory pathways and projects mostly to a localized (discrete) region of the cortex - focal projection Nonspecific projection system of thalamus Nonspecific thalamic nuclei receive afferent fibers from reticular formation and send fibers to very broad regions of cortex - diffuse projection Sensory areas of cerebral cortex Somatic sensory information in venter posterior nucleus are projected onto specific area of cerebral cortex though specific projection system, the area is called the somatic sensory area, mainly including somatosensory area and proprioception area. Sensory Area of Cerebral Cortex 1. Somatosensory area Primary somatosensory area The sensory projection rules: Located in the postcentral gyrus What is Sensory column? Second Somatosensory area Sensory Area of Cerebral Cortex 1. Somatic sensory area 2. Proprioception area Somesthesia 1. Touch & Pressure sensation Two afferent pathways: medial lemniscus and anterior lateral lemniscus. Only wide central damage can block completely the sensation. Touch and pressure types in two pathways are different: When pathways damaged 2. Proprioception 3. Temperature sensation 4. Pain sensation Part 7 Control of Motor Function Somatic movement Motor functions of the spinal cord Anterior Anterior motor neurons horns of the cord gray matter Types of motor neurons motor neuron motor nerve fiber large skeletal muscle fibers Final road of the cord reflex A motor neuron A motor nerve fiber intrafusal fibers β-motor neuron Motor unit A single nerve fiber + skeletal muscle fibers Spinal shock The spinal cord reflexes Stretch reflex Flexor reflex Crossed extensor reflex Types of stretch reflex 1. Tendon reflex (dynamic stretch reflex) Rapid stretchinstantaneous, strong reflex contraction Monosynaptic reflex 2. Muscle tonus (static stretch reflex) Slow stretch weaker continuous contraction Polysynaptic reflex Reflex arc of stretch reflex 1. Sensory receptors Muscle spindle Intrafusal fibers Nuclear bag muscle fiber Nuclear chain fiber Stimulation: Muscle length or rate of change of its length Intrafusal fibers: Golgi tendon organ Stimulation: Tendon tension or rate of change of tension Providing a negative feedback 2. Afferent fibers of stretch reflex Muscle spindle Ia fiber II fiber (flower-spray ending) Golgi tendon organ Ib fiber 3. Neural center: anterior motor neurons Efferent fibers: large motor nerve fibers or small motor nerve fibers 4. 5. Effector: extrafusal skeletal muscle fibers Summary of stretch reflex 1) When the stretch receptors fire, the a-motor neuron is excited, and the muscle contracts 2) When the Golgi tendon organ fires, the a-motor neuron is inhibited (via an inhibitory interneuron), and the muscle relaxes Flexor reflex Nociceptive reflex, withdrawal reflex or pain reflex A spinal reflex intended to protect the body from damaging stimulus, and is polysynaptic Crossed extensor reflex Brain stem control of motor function Brain stem Medulla, pons, and mesencephalon Reticular system Facilitatory and inhibitory area Regulation of muscle tonus Facilitatory & inhibitory area Decerebrate rigidity Sectioned below the midlevel of the mesencephalon Antigravity muscles Neck, trunk and extensors of the legs Decorticate rigidity Decorticate rigidity (A, B, C) A: supine position. head pose is normal, upper limbs is half flexion; B and C: the upper limb posture in rotating the head ; Decerebrate rigidity (D) Both upper and lower limbs are stiff. Mechanism of decerebrate rigidity Alpha rigidity: alpha rigidity is caused by the descending function of high center to increase alpha motor neuron activity. Alpha rigidity is mainly realized through the vestibulospinal tract. Gamma rigidity: gamma rigidity is caused by the descending function of high center to firstly increase gamma motor neuron activity then alpha motor neuron activity. Gamma rigidity is mainly realized through the reticulospinal tract. Brain stem regulation to posture Attitudinal reflex Tonic labyrinthine reflex: Tonic neck reflex: Righting reflex CNS Regulation to Somatic Motor 1. Production of voluntary movement 2. Cortical motor area Primary motor area Primary motor area Its function characteristics Other motor area 3. Efferent Pathway of Cerebral Cortex Including corticospinal tract and corticonuclear tract Corticospinal tract Cortex lateral funiculus of spinal cord : Cortex anterior funiculus of spinal cord: Corticonuclear tract Efferent pathway injury Babinski sign 4. Motion Regulatory Function of Basal Ganglia Structure of Basal Ganglia Connection between basal ganglia and cerebral cortex Direct pathway and indirect pathway DA: dopamine GABA: gammaaminobutyric acid GLu: glutamate (+): excitatory effect (-): inhibitory effect Nigrostriatal dopaminergic projection system Parkinson’s disease Parkinson’s disease Huntington disease What is Huntington's Disease? Symptoms: Pathological mechanism : 5. Motion Regulatory Function of Cerebellum Structure of Cerebellum Vestibulocerebellum Spinocerebellum Corticocerebellum The central analysis to visceral sensation Afferent Pathway and Cortical Area Visceral sensation 1. Characteristics of visceral pain: 2. Parietal pain 3. Referred pain Mechanism of referred pain The central analysis to special sensation Vision 1. Afferent pathway Vision 2. Visual cortex Visual cortex structure Orientation column Auditory sensation 1. Afferent pathway Auditory sensation 2. Auditory cortex