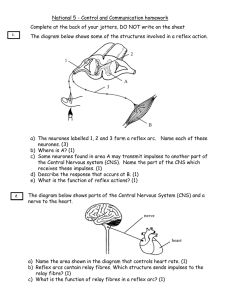
The Reflex Arc Starter: Why does our body have to feel pain? Our learning objectives Describe the role of the nervous system Describe the structures involved in a pain withdrawal reflex arc Explain the pathway taken in a pain withdrawal reflex https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UtEqmmLJstg We met these words last lesson, can you match the definition to the word? A) Receptor 1) A name for a nerve cell B) Effector 2) A muscle or organ that brings about a change C) Coordination Centre 3) Receives information from the receptors and organises the response e.g. brain or spinal cord D) Neurone 4) Detects changes in the environment (known as stimuli) We met these words last lesson, can you match the definition to the word? A) Receptor 1) A name for a nerve cell B) Effector 2) A muscle or organ that brings about a change C) Coordination Centre 3) Receives information from the receptors and organises the response e.g. brain or spinal cord D) Neurone 4) Detects changes in the environment (known as stimuli) Think of some famous arches… A reflex arc follows a very similar shape There are various types of neurones: 1)Sensory neurons 2)Relay neurones (interneurons) 3)Motor neurones https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nKPEW-ao2Wg Name the 5 senses… Sensory neurones carry the information from receptors which can tell if there is a change in one of senses that can be detected (these stimulate the receptor). The 5 main senses are: Touch Sight Hearing Taste Smell Relay neurone Passes message on from sensory neurone Because they are not directly connected, a chemical is released across the junction (or synapse) Motor neurone The motor neurone goes from the relay neurone to the effector (the muscle or gland) Now you’re going to test some basic reflexes as well You will have just 3 minutes with each reflex. With reflex you should: Write down what the stimulus is (what is being sensed?) Light, touch etc. What does the reflex protect you from? Reflex arcs Reflex Knee-jerk Iris (muscles in eye) Gag reflex The ‘Startle’ Reflex Stimulus (what change is detected?) What does this protect? Tendons below knee cap are stretched Balance Reflex arcs Reflex Stimulus (what change is detected?) What does this protect? Knee-jerk Tendons below knee cap are stretched Balance Iris (muscles in eye) Light intensity (level of light) Stops eye damage Gag reflex Touching back of throat/tongue Choking The ‘Startle’ Reflex Loud noise Potential danger Plenary – whiteboards ready 1. How would you describe a reflex arc? a) Slow and voluntary b) Fast and voluntary c) Fast and automatic 2. Where are responses coordinated during a reflex arc? a) Brain b) Spinal Cord c) Pancreas 3. What is the correct order that impulses are sent through neurones? a) Sensory, Relay, Motor b) Motor, Relay, Sensory c) Sensory, Motor, Relay 4. What happens at the junction where one neurone meets another? a) The neurones are connected b) A chemical signal is released c) The impulse stops Plenary – whiteboards ready 1. How would you describe a reflex arc? a) Slow and voluntary b) Fast and voluntary c) Fast and automatic 2. Where are responses coordinated during a reflex arc? a) Brain b) Spinal Cord c) Pancreas 3. What is the correct order that impulses are sent through neurones? a) Sensory, Relay, Motor b) Motor, Relay, Sensory c) Sensory, Motor, Relay 4. What happens at the junction where one neurone meets another (synapse)? a) The neurones are connected stops b) A chemical signal is released c) The impulse