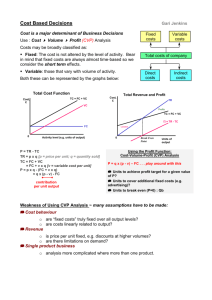
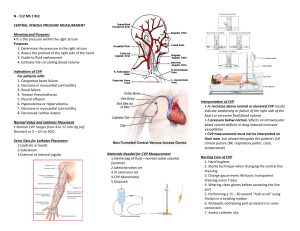
400000 $200 Contribution margin $400000 $200
advertisement

What are the components of cost–volume–profit (CVP) analysis? How does a CVP income statement help management make decisions? The CVP income statement is helpful to management for internal use. The information can allow management to make estimate for future costs, and revenues to help forecast and plan for operations activities, and the performance of the business. Management is concern with the cost of products, volume of sales, the selling price per unit, sale mix, and the profits. Example, Boo Enterprise is selling a new and improved texting card, management will use this information to determine what step need to be taking for the business to remain profitable. The information below shows that Boo Enterprise has a net income of $300,000 thus the company is making a profit. Boo Enterprise could use this information toward a strategy to double the sale for the next fiscal year. Texting Cards Unit selling price $400 Variable cost $200 Total monthly fixed cost $100,000 Total unit sold 2,000 Boo Enterprise CVP Income Statement For the Month Ended April 30, 2012 Total Sales (2,000 texting cards) Per Unit $800,000 $400 Variable costs $400,000 $200 Contribution margin $400,000 $200 Fixed costs $100,000 Net Income $300,000 Reference Kimmel, P. D., Weygandt, J. J., & Kieso, D. E. (2009). Accounting: Tools for business decision making (3rd ed.). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons