Chapter 3: CVP Analysis Horngren 13e 2 -1

Horngren 13e
Chapter 3:
CVP Analysis
2 -1
3-2
3-3
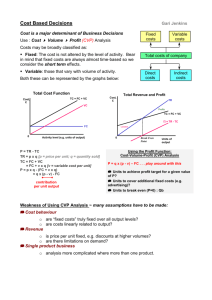
Learning Objective 1. Explain the features of cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis . . . how operating income changes with changes in output level, selling prices, variable costs, or fixed costs
Learning Objective 2. Determine the breakeven point and output level needed to achieve a target operating income . . . compare contribution margin and fixed costs
[EXERCISE]
3-4
Learning Objective 1. Explain the features of cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis . . . how operating income changes with changes in output level, selling prices, variable costs, or fixed costs
Learning Objective 2. Determine the breakeven point and output level needed to achieve a target operating income . . . compare contribution margin and fixed costs
[SOLUTION]
3-5
Learning Objective 3. Understand how income taxes affect CVP analysis . . . focus on net income
Learning Objective 4. Explain CVP analysis in decision making and how sensitivity analysis helps managers cope with uncertainty . . . determine the effect on operating income of different assumptions
[EXERCISE]
Alex Miller, Inc., sells car batteries to service stations for an average of $30 each.
The variable cost of each battery is $20 and monthly fixed manufacturing costs total $10,000. Other monthly fixed costs of the company total $8,000.
Required: a. What is the breakeven point in batteries?
b. What is the margin of safety, assuming sales total $60,000?
c. What is the breakeven level in batteries, assuming variable costs increase by 20%?
d. What is the breakeven level in batteries, assuming the selling price goes up by 10%, fixed manufacturing costs decline by 10%, and other fixed costs decline by $100?
3-6
Learning Objective 3. Understand how income taxes affect CVP analysis . . . focus on net income
Learning Objective 4. Explain CVP analysis in decision making and how sensitivity analysis helps managers cope with uncertainty . . . determine the effect on operating income of different assumptions a.
b.
c.
d.
N = Breakeven units
$30N - $20N - $10,000 - $8,000 = 0
$10N - $18,000 = 0
N = $18,000/$10 = 1,800 batteries
[SOLUTION]
Margin of safety = $60,000 - ($30 × 1,800) = $6,000
N = Breakeven units
$30N - $24N - $10,000 - $8,000 = 0
$6N - $18,000 = 0
N = $18,000/$6 = 3,000 batteries
N = Breakeven units
$33N - $20N - $9,000 - $7,900 = 0
$13N - $16,900 = 0 N = $16,900/$13 = 1,300 batteries
3-7
Learning Objective 5. Use CVP analysis to plan variable and fixed costs . . . compare risk of losses versus higher returns
[EXERCISE]
3-8
Learning Objective 5. Use CVP analysis to plan variable and fixed costs . . . compare risk of losses versus higher returns
[SOLUTION]
3-9
Learning Objective 6. Apply CVP analysis to a company producing multiple products
. . . assume sales mix of products remains constant as total units sold change
[EXERCISE]
3-10
Learning Objective 6. Apply CVP analysis to a company producing multiple products
. . . assume sales mix of products remains constant as total units sold change
[SOLUTION]
3-11