Classification of Matter
advertisement

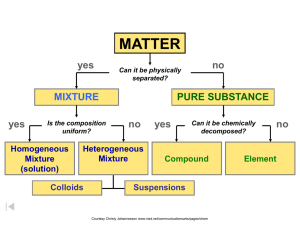
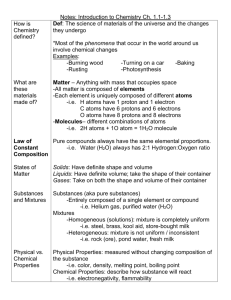
CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER MRS. D’Anton VOCABULARY REVIEW GAME RULES: FAMILY FEUD STYLE 1. Class is divided into 2 teams. 2. Each team sends 1 representative to the whiteboard. 3. A definition is projected and read aloud. 4. The first person to correctly spell the word on the white board, and pronounce correctly, gets the point. 5. The second team may steal if there is an incorrect spelling or pronunciation. 6. Class should check their homework and ensure the correct spelling of the word and definition is written in their notes during the game. VOCABULARY WORD CLUE The smallest unit of a substance that keeps all of the physical and chemical properties of that substance; it ca consist of one atom or two or more atoms bonded together. VOCABULARY WORD CLUE A sample of matter, either a single element or a single compound that has definite chemical and physical properties VOCABULARY WORD CLUE The smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element VOCABULARY WORD CLUE A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined VOCABULARY WORD CLUE A substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical means; all atoms of this have the same atomic number VOCABULARY WORD CLUE Describes something that has a uniform structure or composition throughout VOCABULARY WORD CLUE A substance made up of atoms or 2 or more different elements joined together by chemical bonds VOCABULARY WORD CLUE Composed of dissimilar components. CLASSIFYING MATTER Everything is composed of matter. -Matter is anything that has mass and volume. -Matter exists in different forms, so classification is important when studying it. -In chemistry, classification can help you predict what characteristics a sample may have based on others like it. Example: By analyzing the properties of salt and water, we can predict how salt water may behave PHYSICAL & CHEMICAL PROPERTIES - Physical properties - characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance. Can you name some physical properties of this cupcake? - Chemical properties - relates to a substance’s ability to undergo changes that transform it into different substances PHYSICAL PROPERTY EXAMPLES - Color - Shape - State - Mass - Texture - Volume - Melting Point - Density - Boiling Point - Hardness - Size - Magnetic Properties CHEMICAL PROPERTY EXAMPLES - Flammability Sample Statements: - Reactivity - Burns in air - Toxicity - Gold does not react with oxygen - Toxic when mixed with x. Matter can be in any state. Solid, Liquid, Gas or Plasma* MATTER yes MIXTURE yes Is the composition uniform? Homogeneous Mixture (solution) PURE SUBSTANCE no Heterogeneous Mixture Colloids no Can it be physically separated? yes Can it be chemically decomposed? Compound Suspensions Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem no Element PURE SUBSTANCES Element composed of identical atoms Can exist as single atoms, molecules or as allotropes. EX: copper wire, aluminum foil Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem PURE SUBSTANCES Compound composed of 2 or more elements in a fixed ratio properties differ from those of individual elements EX: table salt (NaCl) Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem MIXTURES Variable combination of two or more pure substances. Heterogeneous Homogeneous Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem COMPARING/CONTRASTING TYPES OF MATTER Both elements and compounds have a definite makeup and definite properties. Mixtures Elements only one kind of atom; atoms are bonded it the element is diatomic or polyatomic substance with definite makeup and properties Packard, Jacobs, Marshall, Chemistry Pearson AGS Globe, page (Figure 2.4.1) Compounds two or more kinds of atoms that are bonded. two or more substances two or that are physically more mixed and retain kinds of atoms properties of original substances. Can be mixed in various ratios LAW OF DEFINITE PROPORTIONS A given compound always contains the same, fixed ratio of elements Compounds are always represented by an abbreviation or formula. Example: The molecular formula of H2O shows that water molecules always have 2 hydrogen atoms bonded to 1 oxygen atom. LAW OF MULTIPLE PROPORTIONS Carbon, C Carbon, C Oxygen, O Oxygen, O Oxygen, O Carbon monoxide, CO Carbon dioxide, CO2 Elements combine in different ratios to form different compounds. Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem MORE ON MIXTURES A sample of matter than contains two or more pure substances is a mixture. Examples: - Air - Sweetened Ice Tea - Salad - Salt Water - Milk - Alloy TYPES OF MIXTURES: SOLUTION SOLUTION Homogeneous mixture Very small particles- uniform distribution No Tyndall effect Tyndall Effect – particles don’t settle – EX: rubbing alcohol Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem MIXTURES COLLOID Heterogeneous Mixtue Medium-sized particles Tyndall effect Particles don’t settle (suspended) EX: milk Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem MIXTURES SUSPENSION Heterogeneous Mixture Large particles Tyndall effect Particles settle EX: fresh-squeezed lemonade /orange juice Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem IDENTIFY THE SUBSTANCE hydrogen atoms IDENTIFY THE SUBSTANCE IDENTIFY THE SUBSTANCE oxygen atoms hydrogen atoms IDENTIFY THE SUBSTANCE LET’S PRACTICE – PROBLEM #7 #7. Identify each of the following as an element, compound, homogenous mixture or heterogeneous mixture. - CH4 - S8 -Distilled Water - Salt Water - CH2O - Concrete INDEPENDENT PRACTICE Please try the following: Please try the following: #5. What is the smallest number of elements needed to make a compound? # 14. Four different containers are labeled C + O2, CO, CO2 and Co. Based on these labels, classify each as a: - compound -element -heterogeneous mixture -homogeneous mixture