06MolecularGeometryandBondingSLrevSept2012
advertisement

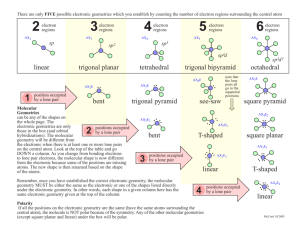
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories AP Chemistry – Ch 9 Mr. Christopherson VSEPR Theory Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs orient themselves around the central atom in order to minimize repulsive forces. They get as far apart from each other as possible. Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem VSEPR Theory Types of e- Pairs Bonding pairs - form bonds Lone pairs - nonbonding electrons Lone pairs repel more strongly than bonding pairs!!! Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem VSEPR Theory Lone pairs reduce the bond angle between atoms because they repel more strongly than bonding pairs. Bond Angle Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Determining Molecular Shape Draw the Lewis Diagram. Count up e- pairs on central atom. double/triple bonds = ONE pair Shape is determined by the # of bonding pairs and lone pairs. Know the 8 common shapes & their bond angles! Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Molecular Shapes AB2 Linear AB4 Tetrahedral AB3 Trigonal planar AB3E Angular or Bent AB3E Trigonal pyramidal AB2E2 Angular or Bent The VSEPR Model The Shapes of Some Simple ABn Molecules SO2 .. O N S O C O O Linear O Bent F S O F F O Trigonal planar Trigonal pyramidal SF6 F F F F F Square planar Brown, LeMay, Bursten, Chemistry The Central Science, 2000, page 305 F F P Xe F F F S F F F F F Trigonal bipyramidal Octahedral Bonding and Shape of Molecules Number of Bonds Number of LONE Pairs 0 3 0 4 0 3 1 2 2 Shape Examples -Be- Linear BeCl2 Trigonal planar BF3 Tetrahedral CH4, SiCl4 Pyramidal NH3, PCl3 Bent H2O, H2S, SCl2 B C : 2 Covalent Structure : N O: Molecular Geometry 180o 109.5o Trigonal planar Linear Tetrahedral 107.3o Trigonal pyramidal 104.5o Bent H2O CH4 PCl3 BeH2 BF3 CO2 H H CH4 H C H H molecular formula structural formula H C 109.5o H H molecular shape H C H H H tetrahedral shape of methane tetrahedron ball-and-stick model Methane & Carbon Tetrachloride molecular formula structural formula molecular shape H CH4 H C ball-and-stick model H H H H C 109.5o H H Cl CCl4 Cl C Cl Cl space-filling model H H .. .. C N O 109.5o H H H CH4, methane lone pair electrons 107o H H 104.5o H NH3, ammonia H2O, water .. O O O O O3, ozone H O O Common Molecular Shapes 2 total 2 bond 0 lone B A B LINEAR BeH2 180° Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Examples CO2 2 total 2 bond 0 lone O C O LINEAR 180° Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Common Molecular Shapes 3 total 3 bond 0 lone B A B B BF3 TRIGONAL PLANAR 120° Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Common Molecular Shapes 3 total 2 bond 1 lone SO2 BENT <120° Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Common Molecular Shapes 4 total 4 bond 0 lone B A B B B CH4 TETRAHEDRAL 109.5° Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Common Molecular Shapes 4 total 3 bond 1 lone NH3 TRIGONAL PYRAMIDAL 107° Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Examples PF3 4 total 3 bond 1 lone F P F F TRIGONAL PYRAMIDAL 107° Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Common Molecular Shapes 4 total 2 bond 2 lone H2O BENT 104.5° Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Common Molecular Shapes Ba 5 total 5 bond 0 lone Be Be Be Ba PCl5 TRIGONAL BIPYRAMIDAL 120°/90° Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem Common Molecular Shapes 6 total 6 bond 0 lone B B A B B B B SF6 OCTAHEDRAL 90° Courtesy Christy Johannesson www.nisd.net/communicationsarts/pages/chem