Cell Membrane
advertisement

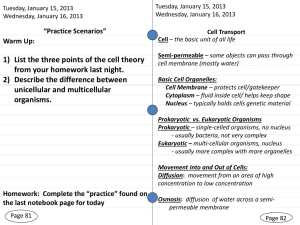
Tuesday, January 15, 2013 Wednesday, January 16, 2013 “Practice Scenarios” Warm Up: 1) List the three points of the cell theory from your homework last night. 2) Describe the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Tuesday, January 15, 2013 Wednesday, January 16, 2013 Cell Transport Cell – the basic unit of all life Semi-permeable – some objects can pass through cell membrane (mostly water) Basic Cell Organelles: Cell Membrane – protects cell/gatekeeper Cytoplasm – fluid inside cell/ helps keep shape Nucleus – typically holds cells genetic material Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Organisms Prokaryotic – single-celled organisms, no nucleus - usually bacteria, not very complex Eukaryotic – multi-cellular organisms, nucleus - usually more complex with more organelles Movement Into and Out of Cells: Diffusion: movement from an area of high concentration to low concentration Homework: Complete the “practice” found on the last notebook page for today Page 81 Osmosis: diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane Page 82 Using Energy to Transport Materials Across the Cell Membrane Two Main Categories: Passive Transport/Diffusion (usually small particles) – Moves substances from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration Example: Food coloring added to a beaker of water: before after Active Transport (usually larger particles) – Relies on the cell using energy (ATP) to move particles across the membrane Three Categories: 1. Transport Proteins: Special proteins use energy/ATP to pump materials into cell (gatekeeper) 2. Endocytosis: membrane surrounds particles to move them inside (see diagram on next slide) 3. Exocytosis : release of substances from inside vesicles through joining and then releasing from the cell membrane (see diagram on next slide) Exchanging materials between the cell and its environment Passive Transport Diffusion Active Transport Transport Proteins use ATP Endocytosis (reverse for Exocytosis) Osmosis Video’s and Examples Passive and Active Transport Animations Endocytosis and Exocytosis Animation Homework/Practice DIRECTIONS- First Identify if the process is moving materials by active or passive transport. Then determine if the process is diffusion, osmosis, transport proteins, endocytosis, or exocytosis. 1. WATER MOVES OUT OF PLANT LEAF, CAUSING IT TO WILT AND DRY. 2. IF YOU PLACE A TEA BAG IN WATER AND TEA IS MADE. 3. IF FOOD THAT IS TOO LARGE TO ENTER THROUGH THE CELL MEMBRANE IS BROUGHT INTO THE CELL TO KEEP IT FROM DYING. 4. YOU SMELL THE DELICIOUS ODOR OF BAKING COOKIES BEFORE YOU ENTER THE KITCHEN. 5. FRESH WATER MOVES INTO A SINGLE CELLED ORGANISM. 6. A ONE CELLED AMEOBA SURROUNDS A PARTICLE OF FOOD. 7. EXCESS SALT THAT AN IGUANA HAS SOAKED UP IN THE OCEAN IS REMOVED THROUGH THE NOSTRILS. 8. IF A PLANT PUMPS MINERALS FROM THE SOIL TO THE ROOT OF THE PLANT. Thursday, January 17, 2013 Friday, January 18, 2013 Organelle Chart Warm –up 1. How are the various jobs in a town or a company divided up among people? Provide examples. 2. Why is it effective to divide the labor in this way? Thursday, January 17, 2013 Friday, January 18, 2013 Organelle Scavenger Hunt - BYOT Organelle: – parts of a cell with specific function – structure in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell that can act as a storage site, process energy, move materials, or manufacture substances Mini-web quest using www.cellsalive.com www.biology4kids.com Homework: Create chart of cell organelles and their functions Tell whether the part is in plant, animal, or both cells Page 83 Page 84 Wednesday, January 23, 2013 Thursday, January 24, 2013 Wednesday, January 23, 2013 Thursday, January 24, 2013 Make a Cell Concept Map (see below) Warm Up: Job in the Factory Cell Organelle Function of the Organelle Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Assembly line where workers assemble product Finishing/ Packaging department Power Source Cell Organelle Quiz and Cell Cycle Notes Respiration and Photosynthesis: - reactions are complete opposites of each other Respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2 ATP + 6 H2O + 6 CO2 Photosynthesis: Sun + 6 H2O + 6 CO2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 Turn to pages 48 – 52 of your text book and find the steps of each of these processes. Make a t-chart with a numbered list to explain the reaction step by step. Photosynthesis Respiration Security Guard Homework: Make a concept map with Cell in the middle and 4 spokes coming out titled: division, transport, animal and plant. List the vocabulary words we’ve done in class under the specific category Page 85 they belong to. 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. Page 86 Wednesday, January 23, 2013 Thursday, January 24, 2013 Wednesday, January 23, 2013 Thursday, January 24, 2013 Cell Organelle Quiz and Cell Cycle Notes Warm Up: Job in the Factory Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Assembly line where workers assemble product Finishing/ Packaging department Power Source Security Guard Cell Organelle Function of the Organelle Cell cycle - normal sequence of the development and division of a cell Three main stages: 1) Interphase - cell is performing normal functions and preparing to divide - the longest part of the cycle - cell grows about twice its original size - goes about regular cell activities - DNA is copied to prepare for mitosis 2) Mitosis - nucleus splits and divides - prokaryotes do not do this (no nucleus) - usually the shortest period in cycle - goal of mitosis is to transfer DNA and other cell structures from parent cell to new cell 3) Cytokinesis – occurs directly after mitosis - parent cell pinches off - two genetically identical cells form Homework: Page 85 Page 86 Cell Cycle Mitosis Cytokinesis Interphase Interphase Helpful Animation Interphase Cell Cycle Diagram Interphase Cytokinesis Mitosis Friday, January 25, 2013 Monday, January 28, 2013 “Find the Cell Phrase” worksheet Warm –up Friday, January 25, 2013 Monday, January 28, 2013 Relooping and Steps of Mitosis Mitosis notes – See pg 82 E and handout with diagrams or animation below 1. Turn to Textbook page 68E and answer questions 25 – 27. Homework: 1. “Find the Cell Phrase” worksheet Page 87 Good Mitosis Animation Page 88