Memmler*s A&P
advertisement

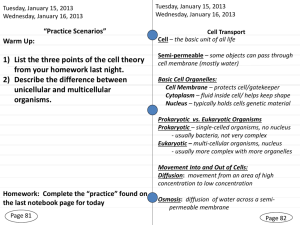
Memmler’s A&P Chap 3 Cells and their functions Generalized animal cell p37-38 •Plasma membrane •Nucleus •Cytoplasm •Endoplasmic reticulum: •Ribosomes •Mitochondria •Lysosomes •Vesicles •Centrioles •Cilia •Flagellum Plasma membrane p37-39 •regulates what comes into the cell and what goes out of the cell. •Functions of proteins in the plasma membrane: •Channels •Transporters •Receptors •Enzymes •Linkers •Cell identity markers Cellular diversity p41-42 Protein synthesis p41 • Ribosomes and RNA synthesize protein • Protein synthesis is necessary because most body tissues are built from protein. DNA Table 3-3 page 43 •deoxyribonucleic acid •DNA contains our genetic blueprint for all of our cells •Its shape is a doublestranded helix Mitosis p45-47 (somatic cell division) •When the cell is not dividing, it is in interphase •DNA replicates during interphase. •A typical cell lives in interphase for most of its cycle and spends only a relatively short period in mitosis. •Mitosis •Prophase •Metaphase •Anaphase •Telophase Movement of substances across the plasma membrane p47-48 • Passive transport: no cellular energy is required for passive transport Diffusion p48 Diffusion through a semipermeable membrane p48 Osmosis p48 • Water moves from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. • Think of it as the solutes pulling the water toward them. Water follows salt. Filtration p48 • Passage of water and dissolved materials through a membrane as a result of a mechanical “pushing” force on one side. • The force that causes filtration in the body is always the pressure of blood. Facilitated diffusion p48 Movement of substances across the plasma membrane p49-50 Active transport • Endocytosis • Exocytosis Endocytosis p50 • Phagocytosis • Pinocytosis Exocytosis p51 Effect of osmosis on cells p51-52 Cell aging p51-52 • Programmed cell death: apoptosis • • • • • • Heredity Chemicals Ionizing radiation Physical irritation Diet Viruses Cancer risk factors p52