Labour Market
advertisement

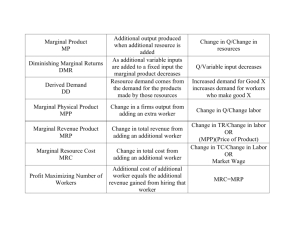
Starter 1. Explain what derived demand is. 2. Give 3 determinants of labour demand and explain each. 3. Economic labour market articles Aims and Objectives Aims: 0 Analyse and Evaluate MRP theory. Objectives: 0 Define MP, MR, and MRP. 0 Describe the relationship between MRP and Diminishing marginal returns. 0 Explain the MRP curve. 0 Analyse shifts in the demand curve for labour. 0 Evaluate MRP theory. Marginal Productivity Theory The demand for labour depends on it’s marginal revenue product. MRP: the value of the physical addition to output arising from hiring one extra worker or F of P. Where the marginal cost of hiring another worker equals its MRP, the equilibrium qty of labour is established. MRP MRP = MP X MR MP = Marginal Product is the number of extra units of output a firm gains from one extra unit of labour. MR = Marginal Revenue is the amount of extra revenue generated from one extra unit of labour. Diminishing Marginal Returns Complete the table Comment on any relationships you notice Draw a graph plotting number of workers and MRP. Comment on any relationships you notice Plot profit on the same graph and comment. Marginal Marginal No Of Product (Total Total Marginal Revenue Margina Total Worker Product x Product Revenue Product (MR x l Cost Revenue s Total Product MP) y) Total Profit Cost 1 12 12 5 60 100 60 100 -40 2 26 14 5 70 100 130 200 -70 3 50 24 5 120 100 250 300 -50 4 90 40 5 200 100 450 400 50 5 140 50 5 250 100 700 500 200 6 200 60 5 300 100 1000 600 400 7 254 54 5 270 100 1270 700 570 8 304 50 5 250 100 1520 800 720 9 340 36 5 180 100 1700 900 800 10 358 18 5 90 100 1790 1000 790 11 374 16 5 80 100 1870 1100 770 Diminishing Marginal Returns Diminishing Marginal Returns 350 900 800 Marginal Revenue Product 300 700 600 250 500 200 400 Marginal Revenue Product (MR x MP) 300 150 200 100 100 0 50 -100 0 -200 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 No. Of Workers 9 10 11 12 Profit Diminishing Marginal Returns 0 After the employment of the second worker and up to the employment of the ninth worker, each one adds more to revenue than to cost. 0 After the employment of the ninth worker the situation is reversed and each additional employee adds more to costs than to revenue. 0 Why does it decrease? 0 Profit maximised at 9 people. Marginal Revenue Product Curve Wage Rate/ Marginal Revenue Product Wage rate (MC2) W2 Wage rate (MC1) W1 MRP Q2 Q1 Quantity of Labour Marginal Revenue Product Curve 0 Demand curve for labour 0 A firm will demand labour at the point where the MRP = MC (Wage Rate) 0 Wage = W1 firm demands Q1 0 If wage rate rises to W2 demand for labour falls to Q2. 0 MRP rises at first until D.Returns sets in. 0 Firm will not be maximising profit at lower employment level, as if it increases employment it can generate MRP over and above the cost of employing them. Peer Teaching 0 Prepare to teach the rest of the class in pairs the marginal revenue product curve. 0 You must define MRP. 0 Explain what factors may lead to an increase in wage rates from W1 to W2. 0 Draw the diagram. Shifts in the Demand Curve for Labour 0 How would increases or decreases in workers productivity at the Toyota Car Assembly factory in Derbyshire affect Toyota’s demand for labour? Shifts in Demand Curve for Labour Wage Rate/ Marginal Revenue Product To avoid ambiguity demand curves are now straight. MRP = D2 MRP = D1 Quantity of Labour Shifting the Labour Demand Curve 0 Shift to the right if the MRP of labour increases. (i.e. if marginal product of labour/or marginal revenue increases). 0 Eg. The demand for car assembly workers will increase if the productivity of car assembly workers rises. (increased training/price of output rises due to increase in car demand). Critique of MRP Theory 0 Brainstorm in pairs/groups any criticisms you have of this theory. A D Criticisms C B Critique of MRP Theory 0 Measuring MRP is difficult. 0 Work is often carried out in teams which makes it hard to identify to contribution to output of individual workers. 0 Difficult to measure MP of workers in the tertiary sector……how do you measure output of accountants? Plenary 0 Define Marginal Product 0 Define Marginal Revenue Product 0 Draw a marginal revenue product curve. 0 Provide a criticism of this theory.