File
advertisement

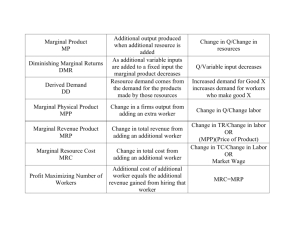
Chapter 25 (and a part of 26) Money-income determination: resource prices help determine income of households Cost minimization: firms base decision off of resource prices in order to maximize profit and minimize cost Resource allocation: firms allocate resources based on price Derived demand: derived from the products that the resources help produce Strength of demand depends on productivity of resource and market value/price of the good Marginal revenue product=change in total revenue divided by unit change in resource quantity Marginal resource cost=change in total cost divided by unit change in resource quantity MRP=MRC for profit maximizing Demand curve: add individual demand curves for all firms hiring that resource Resource demand derived from product demand and depends on resource productivity Quantities of other resources: marginal product of any resource will vary with quantities of other resources used with it Technological advance: better quality of capital, greater productivity Quality of variable resource: Improvements increase marginal productivity and demand Substitution effect: change in price of resource depends on quantity of resource and if they have substitutes Output effect: Increase in price of one input will increase production costs and reduce level of output Labor demand will increase when: -demand for product increases -productivity increases -price of substitute input increases -price of complimentary input decreases Changes in labor demand affect wage rates and employment -Increase in labor demand: increase in employment Fastest growing occupations are in health care Computerized equipment has decreased need for human labor such as meter readers, telephone operators, and mail clerks Ease of Resource Substitutability ◦ The greater the substitutability of other resources, the more elastic the demand is for a particular resource (ex: voicemail instead of telephone receptionist) Elasticity of Product Demand ◦ The greater the price elasticity of product demand, the greater the elasticity of resource demand The Least-Cost Rule: the cost of any output is minimized when the ratios of marginal product to price of the last units of resources used are the same for each resource The Profit-Maximizing Rule: minimizing cost is not sufficient for maximizing profit, so a firm will achieve profit-maximization when each resource is employed to the point at which its marginal revenue product equals resource price Income gets distributed according to contribution to society’s output Some argue that the distribution of income is too unequal Market imperfections: because of real-world market imperfections, wage rates and other resource prices frequently are not based solely on contributions to output A market in which a single employer of labor has substantial buying (hiring) power It will have the following characteristics: ◦ One single buyer of a particular type of labor ◦ This type of labor is relatively immobile, either geographically or because laborers have to acquire new skills ◦ “wage maker” because the wage it pays varies directly with the number of workers it employs Monopsonies have an upward-sloping labor supply to firm MRC is higher than the wage rate To maximize profit, the monopsonist will employ the number of workers where MRC equals MRP Monopsonies in the US are very rare, but professional sports teams are probably the closest we have