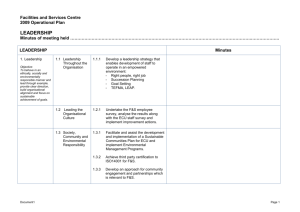
THE CULTURAL WEB OF AN ORGANISATION
advertisement

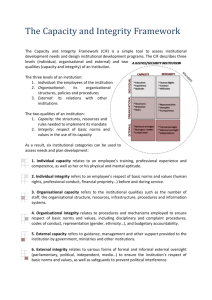
Managing Strategic Change expectations & objectives resource capability environmental forces STRATEGY opportunities & threats strengths & weaknesses SHARED BELIEFS & ASSUMPTIONS STRATEGY Environmental forces Organisational capabilities PERFORMANCE THE CULTURAL WEB OF AN ORGANISATION • STORIES RITUALS & ROUTINES SYMBOLS SHARED BELIEFS AND ASSUMPTIONS CONTROL SYSTEMS POWER STRUCTURES ORGANISATIONAL POWER Managing Strategic Change Managing Transitions Effectively Internal & External Pressures for Change Creating Risk Taking Learning Dealing with Organisational Cultures Managing Organisational Politics Rebuilding Self-Esteem & Performance Achieving Organisational Change & Learning The Transition Curve SENSE OF WELL BEING PERFORMANCE INTEGRATION DENIAL EMOTIONAL TURMOIL SHOCK - FEAR - ANGER - GUILT - GRIEF TIME SEARCH FOR MEANING NEW IDEAS & STRATEGIES ACCEPTANCE LETTING GO OF THE PAST A Model for Managing Change Planning Phase • Generate need • Determine future states • Address organisational power & political dynamics Managing Phase • Disengage from past (and communicate what will not change) • Organise transition management team(s) • Involve organisational members • Use multiple levers • Provide feedback • Create symbols & language EVALUATION Stabilizing Phase • Utilise reward system • Deploy guardians of the new way A Model of Organisational Performance & Change: The TRANSFORMATIONAL Factors EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT MISSION & STRATEGY LEADERSHIP ORGANISATIONAL CULTURE INDIVIDUAL & ORGANISATIONAL PERFORMANCE Eleven Qualities of a Successful Manager Command of basic facts Relevant professional understanding Basic knowledge & information Continuing sensitivity to events Analytical, problem-solving, decision/judgement-making skills Social skills & abilities Skills & attributes THE SUCCESSFUL MANAGER Emotional resilience Proactivity inclination to respond purposefully to events Creativity Mental agility “Meta Qualities” Balanced learning habits & skills Self-knowledge Pedler, Burgoyne & Boydell Force field Analysis FORCES FOR CHANGE STABILITY FORCES AGAINST CHANGE Resistance to Change Individual Resistance • • • • • Habit Security Economic status Fear of the unknown Selective information processing Resistance to Change Organisational Resistance • • • • • • Structural resistance Limited focus of change Group inertia Threat to expertise Threat to established power relationships Threat to established resource allocations Overcoming Resistance to Change • Information through education and communication • Involvement and participation • Support and facilitation – e.g. counselling training • Negotiation • Co-option and manipulation • Coercion • Piloting Six Rules for Managing Change Effectively • Work hard at establishing the need for change • Don’t only think out the change, think through it • Initiate change through informal discussion to get feedback and participation • Positively encourage those concerned to give their objections • Be prepared to change yourself • Monitor the change and reinforce it Ten Organisational Prerequisites for Transformational Change • • • • • • • • Commitment from top leaders Written description of the changed organisation Deconstruct the status quo Identify and mobilise the critical mass for support Need to take a medium to long term perspective Be aware of resistance to change and honour it Develop awareness and education of those affected A passion for change, experimentation and learning is essential from the top • Need to put money where your mouth is! • Maintain open flows of information and communication