Ancient Greece Vocabulary Choice Board - MsKay
advertisement
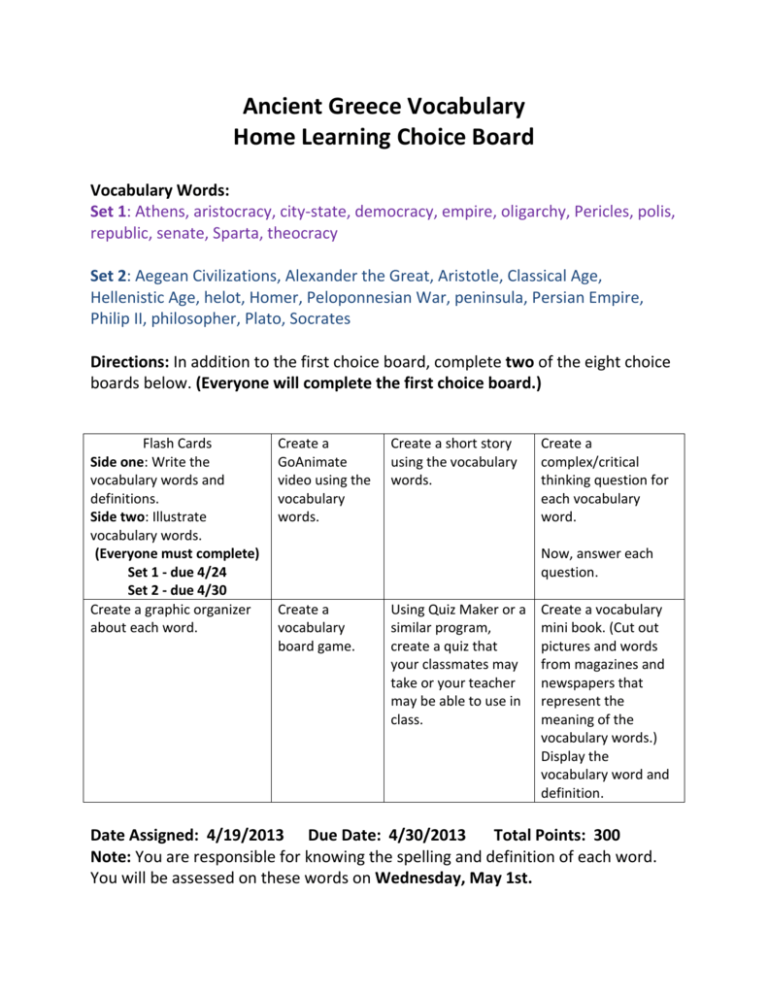
Ancient Greece Vocabulary Home Learning Choice Board Vocabulary Words: Set 1: Athens, aristocracy, city-state, democracy, empire, oligarchy, Pericles, polis, republic, senate, Sparta, theocracy Set 2: Aegean Civilizations, Alexander the Great, Aristotle, Classical Age, Hellenistic Age, helot, Homer, Peloponnesian War, peninsula, Persian Empire, Philip II, philosopher, Plato, Socrates Directions: In addition to the first choice board, complete two of the eight choice boards below. (Everyone will complete the first choice board.) Flash Cards Side one: Write the vocabulary words and definitions. Side two: Illustrate vocabulary words. (Everyone must complete) Set 1 - due 4/24 Set 2 - due 4/30 Create a graphic organizer about each word. Create a GoAnimate video using the vocabulary words. Create a short story using the vocabulary words. Create a complex/critical thinking question for each vocabulary word. Now, answer each question. Create a vocabulary board game. Using Quiz Maker or a similar program, create a quiz that your classmates may take or your teacher may be able to use in class. Create a vocabulary mini book. (Cut out pictures and words from magazines and newspapers that represent the meaning of the vocabulary words.) Display the vocabulary word and definition. Date Assigned: 4/19/2013 Due Date: 4/30/2013 Total Points: 300 Note: You are responsible for knowing the spelling and definition of each word. You will be assessed on these words on Wednesday, May 1st. Ancient Greece Vocabulary Words Set 1 (Government Vocabulary) Athens - A Greek city-state, or polis, famous for its advancements in government and great philosophers Aristocracy - government ruled by nobles, or wealthy citizens City-State - independent regions ruled by the Greek citizens that inhabited them; some citystates were monarchies, aristocracies, democracies, and oligarchies Democracy -government by the people; government in which the supreme power is held by the people and used by them directly or indirectly through representation. Empire - large geographic area under a unified or supreme authority Oligarchy - a government ruled by a small group of individuals whose authority is generally based on wealth or power Pericles - famous leader of Athens who wrote democratic laws and encouraged architecture; the time he ruled Athens is known as the Age of Pericles or the Golden Age of Greece and is considered the period that Greek culture reached its highest level Polis - Greek word for city-state Republic - a form of government where citizens have the power and choose representatives to represent them Senate - a group of citizens who make laws and decisions Sparta - A Greek city-state, or polis, famous for becoming the strongest military power in Ancient Greece Theocracy - a government or country that is ruled by someone who has religious authority or divine right Ancient Greece Vocabulary Words Set 2 Aegean Civilizations - refers to the Hellenes, Minoans, and Trojans; civilizations around the Aegean Sea between 2000 and 1100 BC; the first Greek civilizations that we have much information about Alexander the Great - Philip the II’s son; Macedonian who ruled Greece after his father and eventually conquered all of the Persian Empire, the Middle East, Egypt, and the Indus River Valley; some historians believe he is just a myth Aristotle - 384-322 BC; famous student of Plato who researched logic, politics, and science Classical Age - period that began around 500 BC in which the Ancient Greeks excelled in the arts and sciences and the creation of new forms of government Hellenistic Age - 324-200 BC; period of Greek history marked by great political and cultural change; ruled by Alexander the Great Helot - Spartan slave Homer - famous Greek poet who wrote two famous works of Greek literature, the Iliad and the Odyssey Peloponnesian War - 431-404 BC; war between Sparta and Athens which Sparta eventually won with help from Persia Peninsula - area of land surrounded by water on three sides Persian Empire - powerful ancient empire that controlled all of the Middle East by 522 BC; ruled by King Darius Philip II - king of Macedonia, a nation to the north of Greece, who conquered Greece in 338 BC Philosopher - a scholar who seeks wisdom and truth Plato - 427-347 BC; Socrates’ most famous student; described the ideal form of government in his famous book, The Republic Socrates - 470-399 BC; considered to be the wisest philosopher in Athens; focused on ideas such as virtue, courage, good and evil









