Document
advertisement

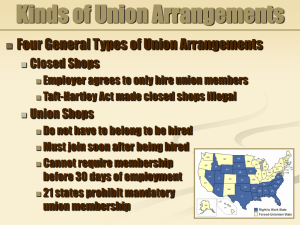
17.1 Chapter 17 Federal Labor Law: Unionization and Collective Bargaining © 2004 West Legal Studies in Business, a Division of Thomson Learning 17.2 Development of Labor Law Unions legalized in late 1800s Sherman Anti-Trust Act of 1890 Clayton Act of 1914 Norris-LaGuardia Act of 1932 National Labor Relations Act of 1935 Taft-Hartley Act of 1947 Landrum-Griffin Act of 1959 National Labor Relations Board Two main functions: Prevent unfair labor practices Settle representation questions Types of proceedings Complaint case (C case) Representation case (R case) Exemptions Federal, state, and local government employees 17.3 17.4 Union-Employee Conflicts Conflict Employer wants the most work done under the cheapest conditions and at the lowest prices Employee wants the highest wages, the best conditions, and the shortest hours Common goal Both want to preserve the company Ways a Union Can Organize 17.5 By voting in a union at a representation election Secret ballots are cast Majority vote is needed By signing authorization cards By the NLRB’s ordering the employer to bargain with a union Preelection Campaign Statements 17.6 NLRA recognizes employees have the right to free speech Employers can state their legal position and views R elections should be conducted in “laboratory conditions” Representation Elections: Election Bar Rule 17.7 Forces employees to think before voting for a union Reduces disruption of employers’ businesses that R elections cause Reduces the drain on NLRB resources Representation Elections: Contract Bar Rule Stops workers from getting rid of or changing unions while contract exists Exceptions Collective bargaining longer than three years Union schism exists or union is defunct Employer has greatly expanded its operations 17.8 Other Court Reviews of NLRB Union Certification 17.9 Runaway shop Bankruptcy to escape collective bargaining agreements Going out of business Duty to bargain Bargaining topics (wages, hours, working conditions) Collective Bargaining Agreement Union negotiates with employer on behalf of the employees Norris-LaGuardia Act prohibits federal courts from issuing injunctions in labor disputes Arbitration, binding arbitration 17.10 17.11 Arbitration Provisions Included in bargaining agreements to settle labor disputes by using neutral third party Courts give great weight to what arbitrator decides May be appealed, but unlikely reversed Devices Affecting Union Security State right-to-work laws Closed shops Union shops Agency shops 17.12 More Measures to Settle Disputes Strikes – used by unions Whipsaw strikes Economic strikes Lockouts – used by employer Secondary boycotts Force someone to stop handling another’s products or doing business with them 17.13 Unions for Government Employees Civil Service Reform Act of 1978 set up Federal Labor Relations Authority Hears complaints from federal workers Hears requests for bargaining in certain issues Most states allow public employees to form unions, but with restrictions 17.14 17.15 Recap – Terms to Know Clayton Act Norris-LaGuardia Act National Labor Relations Act Taft-Hartley Act R cases and C cases Election bar and contract bar rules Right-to-work laws, closed shops, union shops, agency shops Strikes and lockouts