Economic Systems of Europe PPT
advertisement

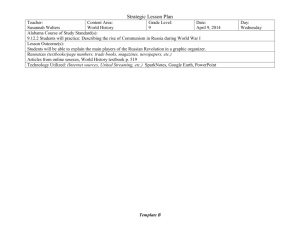
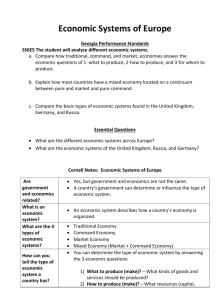
Standard: SS6E5c. Compare the basic types of economic systems found in the United Kingdom, Germany, and Russia. SS6E5a. Compare how traditional, command, and market economies answer the economic questions of (1) what to produce (2) how to produce (3) for whom to produce SS6E5b. Explain how most countries have a mixed economy located on a continuum between pure market and pure command. Use the Economic Systems of Europe Graphic Organizer to record your information Service industries like banking, insurance, and business services account for most of the UK’s gross domestic product Over the decades, the government has turned over many state-owned companies to private ownership setting up free market competition In short, the United Kingdom has a mixed market economy because some of its economy is driven by producers, consumers, and markets while other aspects of its economy are controlled by the government An export-based economy focused on manufacturing and products [relies on global markets] There is also still an issue with updating the Eastern German economy to compete and operate equally with Western Germany [Western Germany invests money in Eastern German states to help modernize and update factories and production lines. West Germany had to bring East Germany’s command economy into its market economy] Germany’s economy combines a market system, some government control, and even social welfare where help is given to the poor Russia has struggled as it transitions from a command economy under the Soviet Union to a mixed market economy today Many government-owned companies are being sold to private businesses, but the Russian government is still largely involved with many aspects of the economy Russia faces financial problems and huge costs to improve its old plants and industries to be more efficient Think, Pair, Share: Answer the question on the bottom of your graphic organizer.