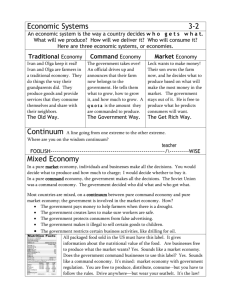
What is an economic system?
advertisement
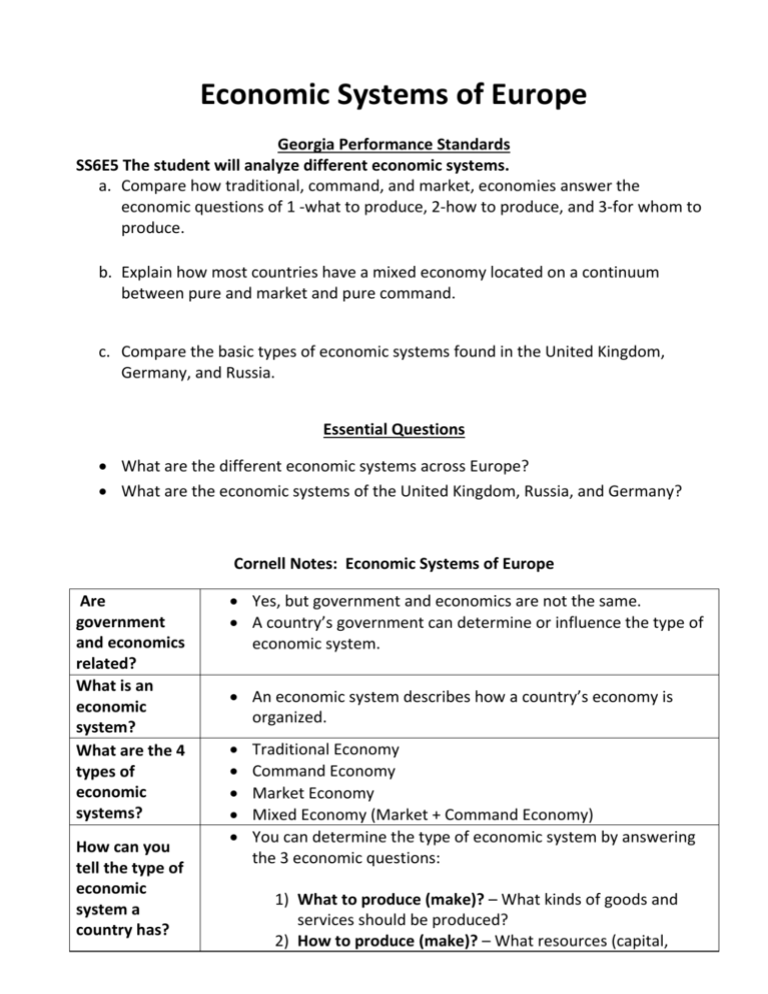
Economic Systems of Europe Georgia Performance Standards SS6E5 The student will analyze different economic systems. a. Compare how traditional, command, and market, economies answer the economic questions of 1 -what to produce, 2-how to produce, and 3-for whom to produce. b. Explain how most countries have a mixed economy located on a continuum between pure and market and pure command. c. Compare the basic types of economic systems found in the United Kingdom, Germany, and Russia. Essential Questions What are the different economic systems across Europe? What are the economic systems of the United Kingdom, Russia, and Germany? Cornell Notes: Economic Systems of Europe Are government and economics related? What is an economic system? What are the 4 types of economic systems? How can you tell the type of economic system a country has? Yes, but government and economics are not the same. A country’s government can determine or influence the type of economic system. An economic system describes how a country’s economy is organized. Traditional Economy Command Economy Market Economy Mixed Economy (Market + Command Economy) You can determine the type of economic system by answering the 3 economic questions: 1) What to produce (make)? – What kinds of goods and services should be produced? 2) How to produce (make)? – What resources (capital, natural) are available to be used to make the goods and services? 3) For whom to produce? – Who gets to have the goods and services? The way a society answers these questions determines its economic system. Who answers the 3 economic questions for the 3 main types of economic systems? Market Economy Who decides What to produce? Who decides How to produce? Who decides For whom to produce? Business – they make products based on the needs of the people in the society (country). If there is no demand for the product, the business will not make it. Business – they decide the best and cheapest way to make the product. The business wants to make a profit (earn money on the products they make). Consumers – the citizens that buy the products. They buy the products based upon their needs, wants, and financial situation. Traditional Economy Government – the People – The government makes customs, traditions, all of the economic and beliefs of the decisions for the people of the citizens. The society. Products citizens have NO are based upon how INPUT on the their ancestors products they would made it. like to buy. Government – The People – The government decides customs, traditions, how the products and beliefs of the are to be made and people of the what they are to be society. Products made with, the are made based cheapest way upon how their possible as to not ancestors made it. cost the government to much money. Government – The People – people in government the village or determines who the society. Bartering products will be (trading or made and given to. exchanging) of goods and services is usually used instead of money. Command Economy Economic Systems Continuum Pure Command Mixed Economy Pure Market No country has a pure command (total government control of everything) and pure market (the freedom to buy and sell anything). All economies are a combination of pure command and pure market economies. Economic Systems of the UK, Germany, and Russia All 3 countries are mixed economies that have some combination of market and command economies. What to produce? United Kingdom Germany Russia Service-based economy (jobs such customer service – cashiers, salespeople, waitress, hair dresser). Agricultural products such as corn, wheat, and soybeans. Germany produces many goods and services that are exported to other countries. Many factories (manufacturing). The Russian government is still very involved with the decisions businesses make. How to produce? Form whom to produce? Businesses have the freedom to make and sell products and services that consumers want to buy. Businesses are independentlyowned (not under government control). Products and services must not be illegal. Businesses have the freedom to make and sell products and services that consumers want to buy. Businesses are independentlyowned (not under government control). Consumers – individuals and business that want to buy the products and services. Consumers can also be international customers (people from other countries). Manufacturing and factories. Consumers – individuals and business that want to buy the products and services. Consumers can also be international Consumers – individuals and business that want to buy the products and services. Consumers can also be international customers (people from other countries). customers (people from other countries). UK Germany Russia 0 Pure Command 51% Mixed Economy 71% 79% 100 Pure Market