KS3 The skeleton[1]
advertisement
![KS3 The skeleton[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009520539_1-3ed9168d9ce09ad3efca8cf7d1e83b85-768x994.png)
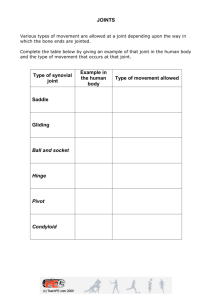
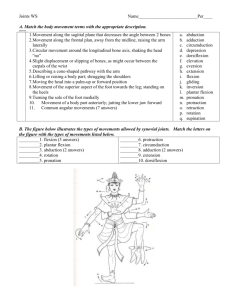
KS 3 Science The Skeleton By M. Burton. Bettws High School, Newport Bones of the human skeleton You do not have to learn the names of all of the bones in the human body ! Functions of the skeleton Support – Your bones give your body its overall shape. Movement – Along with your muscles they allow us to move. Protection – Some bones protect vital organs such as the brain, heart and lungs What is a joint ? A joint is the point where 2 or more bones come together. Types of joint There are many different types of joint in the human body – we will only consider 3 of them ! Fixed Joints Is the skull just one bone ? Fixed Joints The skull is made of 22 bones ! 14 of these are in the face ! The bones of your skull are joined together and cannot move (except the lower jaw). Hinge Joints The elbow joint Allows the arm to bend in one direction Hinge Joints The knee is another type of hinge joint Ball and Socket Joints The hip joint Allows rotation in all directions Ball and Socket Joints Shoulder Hip Can you see another ball and socket joint ? Types of Joints - Summary Copy and fill in this summary table Types of Joints - Summary Type of joint Example Type of movement Fixed Skull None Hinge Knee and elbow Bend in one direction Ball and socket Shoulder and Hip Rotation in all directions Synovial Joints Most joints that allow movement contain liquid and have a similar structure They are called synovial joints and they are full of synovial fluid Synovial Joint Structure ligament ligament Synovial membrane Cartilage Synovial fluid Femur (leg bone) Parts of a Synovial Joint Ligaments – hold bones in place preventing dislocation Synovial fluid – reduces friction as the bones slide across one another Synovial membrane – produces and encases the synovial fluid Cartilage – acts as a shock absorber to protect the ends of the bones