Population Growth: Ecology & Demographics
advertisement

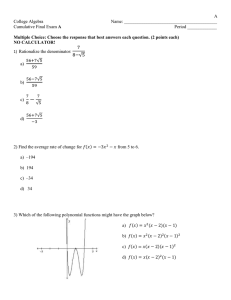
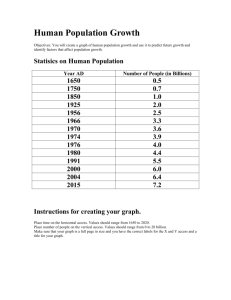
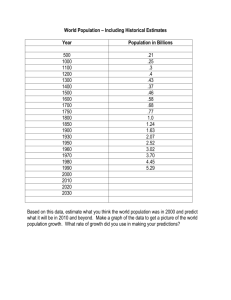
Population Growth Ecology CFU#1 Lesson #3 SWBAT how birth/death rates affect population size. • You will create a graph representing human population growth and use it to predict future growth. • We will analyze the reasons behind this population growth and relate it to ecology concepts such as birth/date rates, population density, and limiting factors. • We will add important population vocabulary to your notes. Setting Up Your Graph… • Your graph should be a full page in size. • Give your graph a title. • Time is the manipulated variable. Place it on the X (horizontal axis.) Values should range from 1650 to 2020, using a constant increment. • Population is the responding variable. Place it on the Y (vertical axis.) Values should range from 0-20 billion, using a constant increment. Plotting the data… Year A.D. Number of People (Billions) 1650 0.5 1750 0.7 1850 1.0 1925 2.0 1956 2.5 1966 3.3 1970 3.6 1974 3.9 1976 4.0 1980 4.4 1991 5.5 2000 6.0 2004 6.4 2012 7 Graph Population (In Billions) World Population Growth 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1650 1700 1750 1800 1850 Year (A.D) 1900 1950 2000 2050 Analysis Questions (Please answer on the back of your graph) • 1.) It took 1649 years for the world population to double, going from 0.25 billion people to 0.5 billion people How long did it take for the population to double once again? • 2.) How long did it take for the population to double a second time? A third time? • 3.) Based on your graph, in what year will the population reach 8 billion? • 4.) Using prior knowledge, what factors have contributed to the world’s overall population growth in the last 150 years? Analysis Answers • 1. It took 200 years for the population to double from 0.5 to 1.0 billion (16501850) • 2. It took 75 years to double from 1 to 2 billion (18501925) and 51 years to double from 2 to 4 billion (19251971) • 3. (Answers will vary, but most estimates are around 2027) • 4. Agricultural revolution resulted in greater growth and transport of food reduced death from starvation. Advances in medicine, sanitation and nutrition reduced death from disease. In your notes… Population Notes • Birth rate- the number of births in a population in a certain amount of time. • Death rate- the number of deaths in a population in a certain amount of time. • Population Statement – If birth rate > death rate, populations increase – If death rate > birth rate, populations decrease • Population Density – Number of individuals ÷ Unit area – Example: 20 monarch butterflies in 10m2 area = 20/10 = population density of 2 monarchs per square meter Population Notes • A limiting factor is an environmental factor that causes a population to decrease. • Some limiting factors for populations are – food & water – Space weather conditions. • Carrying capacity- the largest population that an area can support. Birth Rates… Population Density Population Density • Map showing urban areas with at least one million inhabitants in 2006. Only 3% of the world's population lived in cities in 1800; this proportion had risen to 47% by the end of the twentieth century, and reached 50.5% by 2010