Acid-Base - newshamchemistry

Day 1
Acid-Base
Review of naming acids
Determine Name:
H
2
SO
3
H
2
SO
4
H
2
S
HClO
3
HCl
HClO
2
Determine Name:
H
2
SO
3
H
2
SO
4
H
2
S
HClO
3
HCl
HClO
2
Determine Formula
Hydrofluoric acid
Carbonic acid
Nitrous acid
Hydroselenic acid
Determine Formula
Hydrofluoric acid
HF
Carbonic acid
Nitrous acid
Hydroselenic acid
Characteristics of Acids & Bases
Acids are Characterized by:
O
O
Sour taste
color of indicator
O
O
Release of H
2 gas
Reacts with bases salt( ionic compound) & H
2
O
Bases are Characterized by:
O Bitter taste
O
O
Feels slippery
color of indicator
O
O
Reacts with acid salt( ionic compound) & H
2
O
Conducts electric current ( its an ionic compound)
What does ionization mean?
Ionization
O Adding or removing electrons (e-)
O Making a cation or anion
Strong Acids
O Ionizes completely = breaks up completely
O Conducts electric current
(remember electrolyte demo & PhET)
Strong Acids
Examples:
O Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
O Sulfuric Acid (H
2
SO
4
)
O Nitric Acid (HNO
3
)
Strong Base
O Ionizes completely = breaks up completely
O Examples: group 1 hydroxides – sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, etc.
Neutralization Reaction
HCl + NaOH NaCl + HOH
Strong + Strong Salt + Water
Acid Base
HNO
3
+ KOH KNO
3
+ HOH
Neutralization Reaction
Is a double replacement rxn b/w … strong acid + strong base a salt (ionic compound) + water
pH Scale
Determining strength of an Acid or Base
pH scale 0-14
O neutral pH = 7.0
O acidic pH <7.0
O basic pH > 7.0
pH Scale
Calculating pH & [H + ] pH = -log[H + ]
Inverse of log
10 is 10 ^( )
[H + ] = 10 ^(-pH)
Calculating pOH & [OH ] pH = -log[OH ]
Inverse of log
10 is 10 ^( )
[OH ] = 10 ^(-pOH)
Relationship between pH & pOH pH + pOH = 14
Now you try…
Answer
Try on your own…
Try on your own…
Practice
Now you try
Answer
Try on your own..
Answers
Other methods of determining pH
If molarity is not known, pH can be determined by…
O Acid-Base Indicators
O pH meter
O Titration
Indicator Solutions
O Change color depending on pH of test solution
Indicators
Indicators
Indicators
Problems with indicator solutions:
O If you have a colored solution
O Approx pH value not exact
O Temperature affects color
pH meter
pH meter
O consists of a measuring probe
O electronic meter: measures & displays the pH reading
O have to calibrate probe
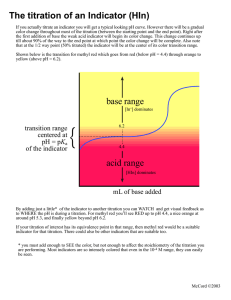
Titration
O Use Buret, Erlenmeyer flask, indicator
O Use M
1
V
1
= M
2
V
2 to determine molarity of unknown
Titration
Titration
Answer the following questions while watching the video clips:
1.
Where do you read/How do you read a burette?
2.
3.
What hand do you use to swirl the Erlenmeyer flask?
What hand do use to adjust the burette?
4.
5.
6.
When do you know you are getting close to the endpoint?
How is the standard solution added as you get close to the endpoint?
When do you know you have achieved the endpoint?
O Titration Video Clip #1 (3:15)
O Titration Video Clip # 2 ( 6:07)
Now, do the titration pre-lab