Acid/Base Chemistry Study Guide: Definitions, Titrations, Buffers
advertisement

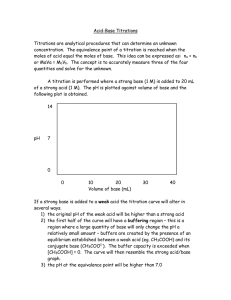
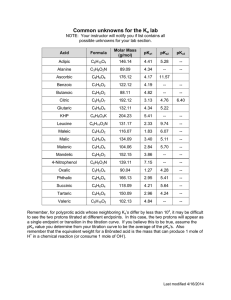
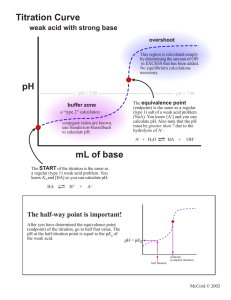
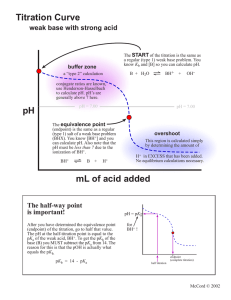
Acid/Base Study Guide: Know the definitions of acids & bases according to Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry. Be able to identify acid/base conjugate pairs. Be able to recognize amphoteric species. Be able to compare Ka and/or Kb values to determine relative strengths of acids or bases. Be able to determine the Ka of a weak acid from a titration curve (remember, pKa = pH at the midpoint of a titration of a weak acid with a strong base). Be able to determine the Kb of a conjugate base given the Ka, or vice-versa. Given different Ka’s of acids, determine which would produce the stronger conjugate base. Know your 7 strong acids and the conjugate base ions that do not affect pH. Given the pH of a solution and the initial concentration of a weak acid or base, determine the Ka or Kb for that acid or base. Given the Ka or Kb of an acid or base and its initial concentration, be able to determine the pH of the solution. Be able to determine the pH of a solution after a chemical reaction (neutralization reaction) has occurred. Recognize how the Ka value of a weak acid can be used to create a buffer within a certain pH range (if [HA] = [A-], then pKa = pH). Know why a certain indicator is used based on its own pKa and the pH of the equivalence point of a titration. Know the definition of the equivalence point. Be able to describe proportion of ions in solution at various points along a titration curve. Be able to derive the Ka or Kb from a titration curve. Be able to determine the pH of a buffer solution given initial concentrations and a Ka value. Be able to determine the pH of a buffer solution after a certain quantity of acid or base is added.