Academic Biology Midterm Study Guide
advertisement

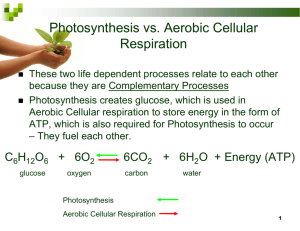
Name Class Date Mid-term Exam Study Guide Chapter 1 – The Science of Biology 1. What is the difference between hypotheses and theories? 2. What are the steps of the Scientific Method? 3. Which big idea in biology is MOST concerned with DNA? 4. Compare and contrast a controlled experiment and an observational study. 5. What are the smallest living objects that biologists study? 6. How many variables are changed in a controlled experiment? 7. List and describe the characteristics of living organisms. 8. What are the two types of reproduction? Describe each. 9. What is evolution? 10. What is homeostasis? Provide an example. 11. How would you determine whether something is living or nonliving? 12. What are the goals of science? 13. What is metabolism? Chapter 2 – The Chemistry of Life 1. What are the three particles that make up an atom and what are their charges? 2. Where are each of the subatomic particles found within the atom? 3. What subatomic particle is responsible for bonding? 4. What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds? 5. Why is water described as a polar molecule? 6. Compare and contrast cohesion and adhesion. Provide an example of each. 7. What type of bond forms between water molecules? 8. List the four macromolecules and their function(s). Macromolecule a. Function b. c. d. 9. What are proteins composed of? 10. Provide at least one example for each of the following: a. b. c. d. CarbohydratesLipidsNucleic AcidsProteins- 11. Describe the following: a. Catalystb. Enzymec. Substrate- Chapter 7 – Cell Structure and Function 1. List the three principles of the Cell Theory. 2. What advance in technology made the discovery of cells possible? 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 4. Provide an example of a prokaryotic and eukaryotic organism. Prokaryotic Eukaryotic- 5. Identify each of the cell structures indicated in the figure below. Use these terms: nucleus, mitochondrion, ribosome, cell membrane, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, Golgi apparatus, cytoplasm. 6. What type of cell is in the image below? _________________ Label A, B, C and D. What is the function of C? 7. Describe the function of each of the following organelles: Nucleus- Lysosome- Rough ER- Smooth ER- Golgi Apparatus- Cytoskeleton- Mitochondria- Chloroplast- Ribosome- Vacuole- Cell membrane- Cell wall- 8. Which sequence correctly traces the path of a protein in the cell? 9. During diffusion, when the concentration of molecules on both sides of a membrane is the same, the molecules will – 10. Describe the effects of osmosis on a cell placed in an isotonic solution, a hypertonic solution and a hypotonic solution. (Drawings would be a good idea.) 11. What is the main difference between passive and active transport? 12. What is ATP? Draw a diagram of ATP and ADP. Label the adenine, ribose, and phosphates. 13. Describe the process of diffusion. 14. This type of passive transport involves the assistance of a membrane protein______________________ 15. Diffusion will occur across a membrane until ________________________ is reached. 16. Describe osmosis. 17. Two main types of active transport are endocytosis and exocytosis. Compare and contrast each type. 18. What are the two types of endocytosis? Describe each. 19. The cells of multicellular organisms are ______________________ to perform different tasks. 20. Describe each of the terms below and provide an example of each. Tissue- Organ- Organ system- Cell- 21. List the levels of organization in a multicellular organism (from question #20) from the simplest level to the most complex level. Chapter 8 – Photosynthesis Please label the following diagram using the terms from the word bank. Thylakoids Calvin Cycle CO2 Granum Light NADPH Stroma H2O ATP Light Dependent Sugar NADP+ Reaction 2. O2 ADP 3. 1. 4. 7. 8. 11. 6. 5. 9. 12. 10. 13. 14. What is the overall equation for photosynthesis? (Use words and chemical symbols.) 15. Describe the relationship between the light dependent cycle and the lightindependent cycle. 16. In what organelle does photosynthesis take place? 17. What are the two phases of photosynthesis? 18. Where does each reaction take place? 19. What do the water molecules get split up into in the light reactions? 20. What is a waste product formed in the light reactions? (We need it to survive!) 21. What two products of the light reactions are used in the Calvin cycle? 22. Label the parts of the chloroplast using the terms in the word bank below. Granum Stroma Thylakoid Space/Lumen Thylakoids Outer Membrane 23. Inner Membrane 24. A. B. C. F. E. D. 24. What is the abbreviation for all the colors of the visible light spectrum? 25. Why do plants appear green? 26. Compare and contrast autotrophs and heterotrophs. Provide examples. 27. What are 3 factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis? Chapter 9 – Cellular Respiration 1. How do organisms get the energy that they need? 2. Photosynthesis occurs in the ____________________________ (organelle) and Cellular Respiration occurs in the ________________________________ (organelle). 3. Define the words aerobic and anaerobic. 4. What role does oxygen play in photosynthesis and cellular respiration? 5. What is the equation for cellular respiration? Write it in symbols and in words. Above the equation label the reactants and the products. 6. List the three stages of respiration? Include the following a) where it occurs b) if it is aerobic or anaerobic c) the total # of ATP molecules produced. __________________ a) __________________ b) __________________ c) _______ ___________________ a) __________________ b) __________________ c) _______ ___________________ a) __________________ b) __________________ c) _______ 7. What is the total number of ATP molecules from the complete breakdown of glucose through cellular respiration? 8. List the 2 electron carriers that are a part of Cellular Respiration/Fermentation and what they convert into. 9. What molecules are formed from glucose during glycolysis? How many of each? _____________________ - _____________ _____________________ - _____________ _____________________ - _____________ 10. Tally up the total amount of ATPs, NADHs, CO2s and FADH2s generated per glucose molecule (REMEMBER, there are 2 ‘turns’ of Krebs cycle because each glucose molecule produces 2 pyruvic acid molecules)? ATP ____________ CO2 ____________ NADH ____________ FADH2 ___________ 11. What molecule passes through ATP synthase to make it spin? 12. When ATP synthase spins, what happens to ADP? 13. When does fermentation occurs and under what conditions? 14. What are the two types of fermentation? Write each of the equations in symbols and in words. Above the equations label the reactants and the products. 15. How do each of the types of fermentation play a role in the lives of humans? 16. Lactic Acid- Alcoholic Fermentation- How do we satisfy our energy needs differently during a sprint or a long run? Chapter 10 – Cell Growth and Division 1. As a cell becomes larger which increases at a faster rate: surface area or volume? 2. What does the rate of waste production in cell depend on surface area or volume? 3. Why do cells need to divide? 4. Describe asexual reproduction. Provide an example(s). 5. Describe sexual reproduction. Provide an example(s). 6. What is the name of the process by which a cell divides into 2 daughter cells? 7. Label the structure to the right and the parts labeled A and B. 8. The main events of the cell cycle are labeled A, B, C, and D in the figure below. Name these events. 9. What is interphase? What phases are a part of this portion of the cell cycle and what happens in each? 10. What is the difference between mitosis and cytokinesis? 11. What is the difference between cell division in plant cells vs. animal cells? 12. What family of proteins in eukaryotes regulates the cell cycle? 13. What is the difference between cancer cells and healthy cells? 14. What does differentiation mean? Chapter 11 Section 4 – Meiosis 1. Define the following terms a. homologous – b. diploid – c. haploid – d. meiosis – e. tetrad – f. crossing over – g. zygote – 2. What are gametes? 3. How are gametes produced and what is different about their chromosomes? 4. How does distance apart on a chromosome affect the inheritance of genes? 5. What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis? 6. What happens to the number of chromosomes per cell during meiosis? 7. Explain why the daughter cells produced during meiosis are genetically different from each other where the daughter cells produced during mitosis are not.