File
advertisement

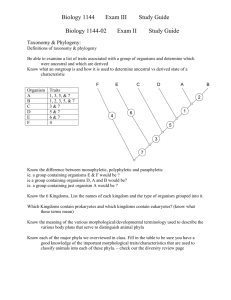
Name: ____________________________________________ Date: ____________________________Hr:______ E.O. #8 Study Guide (Invertebrates) 1. What are the 3 main characteristics for animals? 2. Define a. acoelomate: b. pseudocoelomate: c. coelomate: 3. What does sessile mean? What Phyla have “sessile” individuals? 4. What are the two groups that Animals are grouped into? 5. Using the organisms above, identify what type of symmetry each of them has. 6. What domain do animals belong to? 7. What is cephalization? PHYLUM: PORIFERA 8. What are spicules? 9. How do sponges obtain their food? PHYLUM: CNIDARIA 10. Cnidarians have a ____________________________________________, which is a primitive stomach. 11. The class Scyphozoa, contain what organisms? PHYLUM: PLATYHELMINTHES 12. The Phylum Platyhelminthes have what type of symmetry? 13. What is a proglottid? PHYLUM: NEMATODA 14. What type of body cavity do organisms in the Phylum Nematoda have? 15. They are mutualistic/parasitic worms. PHYLUM: MOLLUSCA 16. The 3-part body plan for the Phylum Mollusca is: 17. Organisms in the Phylum Mollusca are soft-bodied _____________________________ and have a ______________________________ chambered heart. 19. The 3 major Mollusk classes are: PHYLUM: ARTHROPODA 20. Why do arthropods molt? 21. Define chelicerae: 22. Define mandibles: 23. Draw and label an ant below with HEAD, THORAX, and ABDOMEN. 24. COMPARE/CONTRAST incomplete and complete metamorphosis. PHYLUM: ECHINODERMATA 25. ______________________ are tiny legs to help Echinoderms move and grip surfaces. 26. What type of symmetry do adult Echinoderms have? 27. Define ossicles: 28. Choose 4 out of the 8 Invertebrate Phyla we have studied and give one example of an organism we studied in each.