EXAM II 2013
advertisement
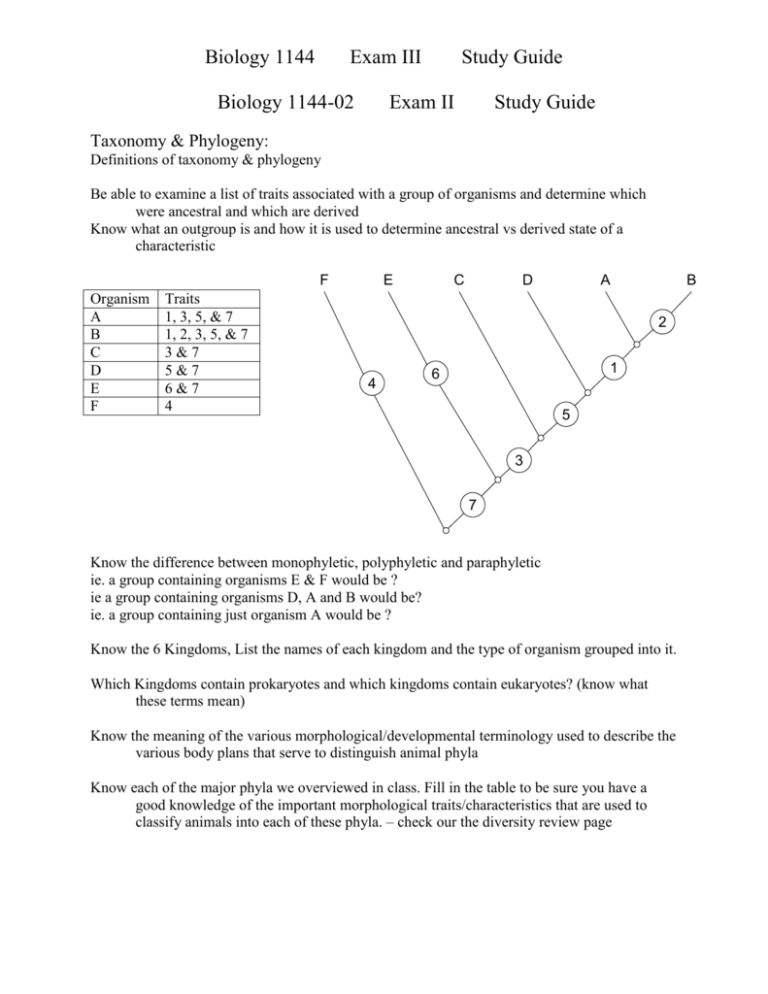
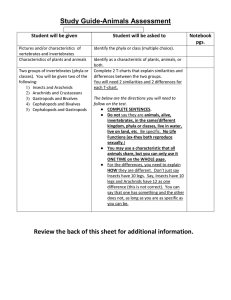
Biology 1144 Exam III Biology 1144-02 Study Guide Exam II Study Guide Taxonomy & Phylogeny: Definitions of taxonomy & phylogeny Be able to examine a list of traits associated with a group of organisms and determine which were ancestral and which are derived Know what an outgroup is and how it is used to determine ancestral vs derived state of a characteristic F Organism A B C D E F Traits 1, 3, 5, & 7 1, 2, 3, 5, & 7 3&7 5&7 6&7 4 E C D A B 2 4 1 6 5 3 7 Know the difference between monophyletic, polyphyletic and paraphyletic ie. a group containing organisms E & F would be ? ie a group containing organisms D, A and B would be? ie. a group containing just organism A would be ? Know the 6 Kingdoms, List the names of each kingdom and the type of organism grouped into it. Which Kingdoms contain prokaryotes and which kingdoms contain eukaryotes? (know what these terms mean) Know the meaning of the various morphological/developmental terminology used to describe the various body plans that serve to distinguish animal phyla Know each of the major phyla we overviewed in class. Fill in the table to be sure you have a good knowledge of the important morphological traits/characteristics that are used to classify animals into each of these phyla. – check our the diversity review page Biology 1144 Phyla Exam III Study Guide Major Distinguishing Characteristic(s) Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda Mollusca Annelida Arthropoda Echinodermata Chordata Protozoa: Kingdom = ?, Eukaryote or Prokaryote? Know the 4 groups we discussed in class AND the major characteristics used to classify protozoans into these groups. Fill in the table below. Phylum/Subphylum Characteristics Describe/Discuss how colonial single cellular organisms could have given rise to simple multicellular organisms. What is the importance of the Volvox spp to this hypothesis? Know the causative protozoans and their vectors for the following parasitic diseases: Malaria African sleeping sickness Chaga’s disease Giardiasis Biology 1144 Exam III Study Guide Symbiosis: What are the three types of symbiosis? (List and define/describe. Think of examples of each type) Phyla: Porifera: ~# of species? Major characteristics ? What characteristics are primarily used to classify poriferans at the Class level within the phylum? List each class we discussed and the characteristic used to define that class In what environment (specifically) would you find the majority of sponges? Give at least one example of how poriferans impact our lives. Cnidaria: ~# of species? Major characteristics? What characteristics are used to classify cnidarians at the Class level within the phylum? List each class we discussed and the characteristic used to define that class Describe the dimorphic lifecycle of a typical hydrozoan or scyphozoan (use of a diagram could be beneficial) Give a general description of the two body forms of cnidarians. Know the following general terms concerning animals in the phyla platyhelminthes, mollusca, & anellida: ecdyzoan lophothrochozoan lophophore trochophore Platyhelminthes: ~# of species? Major characteristics? What characteristics are used to classify platyhelminthes at the Class level within the phylum? List each class we discussed and the characteristic used to define that class. Discuss the general ramifications of a parasitic lifestyle for an organism. Mollusca ~# species major characteristics? What characteristics are used to classify molluscs at the class level within the phylum list each class we discussed and their characteristics Biology 1144 Exam III Study Guide reproductive modes of molluscans – trochophore & veliger larvae for marine bivalves & gastropods; direct development for cephalopoda, glochidia larvae of freshwater bivalves In our lecture, we covered material in addition to the info on the diversity pages for which you will be responsible: class polyplacophora in phylum Mollusca Know major anatomical features of the phyla we discussed (identify on a diagram for example) Platyhelminth: digestive tract of turbellaria, suckers on trematoda, proglottid of cestoda Mollusca: mantle, gills, gut, coelom, heart/circulatory systems General Items to Remember Derived vs ancestral traits. Derived characteristics that set each phylum apart (those listed on the animal kingdom Cladogram on the web page) Embryonic Development Know the stages of embryonic development that we covered in class. These stages are characterized by either distinct morphologies or developmental processes which occur at that time during development. Test your knowledge of this info by completing the table below. Embryonic Stage Processes/Morphology Fertilization – Zygote formation Cleavage Stage Blastula Gastrulation Using the lecture outline and/or textbook, be sure you can describe each of the following items Internal Fertilization vs. External Fertilization . External Development vs. Internal Development .