Brain Anatomy
advertisement

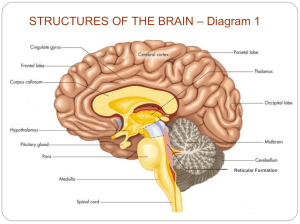
The Brain Structures, Functions, and Injuries Older Brain Structures: Brainstem The Brainstem is the oldest part of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells and enters the skull. It is responsible for automatic survival functions. Medulla The Medulla is the base of the brainstem that controls ___________ and _______________. Pons Involved in coordinating movement, sleeping, waking, and dreaming Brainstem is a crossover point, where most nerves to and from each side of the brain connect with body’s opposite side Reticular Formation Filters incoming stimuli & relays important info to other areas of the brain “Netlike” network of neurons Thalamus Thalamus Sitting atop brainstem Receives information from all senses (except smell) and routes it to the higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting, touching “Hub in which traffics passes en route to various destinations” Thalamus Brain’s sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem. It directs messages to the sensory areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla. Cerebellum The “little brain” attached to the rear of the brainstem. It helps coordinate voluntary movements and balance. Also involved in: nonverbal learning, memory Older Brain Functions “Older” brain functions all occur without any conscious effort Brain processes most information outside of our awareness The Limbic System Limbic System is a doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebrum Associated with emotions such as fear, aggression and drives for food and sex. It includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus. Limbic System Hippocampus: processes memory Injury: . . Amygdala Amygdala: two lima bean-sized neural clusters Influences aggression and fear Processes emotional memories Injury or Damage: . . Hypothalamus Hypothalamus: important link in chain of command governing bodily maintenance Some neural clusters influence: Hunger, Thirst, Body Temp, Sexual Behaviors Monitors both blood chemistry and takes orders from other parts of the brain Limbic System Hypothalamus Directs maintenance activities like eating, drinking, body temperature, and control of emotions. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. Video of an actual brain Hypothalamus = Reward Center Read on page 72 & 73 Olds 1958: located other “pleasure centers” What rats actually experience we don’t know Allowed to press pedals to trigger their own stimulation Feverish pace – 7000 times an hour – until they dropped from exhaustion Reward Center Sanjiv Talwar, SUNY Downstate **Rats cross an electrified grid for self-stimulation when electrodes are placed in the reward (hypothalamus) center (top picture). **When the limbic system is manipulated, a rat will navigate fields or climb up a tree (bottom picture). Reward Center Do humans have limbic centers for pleasure? Neurosurgeon implanted electrodes in such areas Stimulated patients reported mild pleasure However not driven into a frenzy(rat) Researches believe that _____________ disorders may stem from a reward deficiency syndrome Genetically disposed deficiency in natural brain systems for pleasure People crave whatever provides that missing pleasure or relieves negative feelings Mind Control? http://www.learner.org/resources/series142.html?pop =yes&pid=1593 This video links human aggressive behavior with specific regions of the brain. Scenes from classic experiments show stimulation of a bull's brain to stop it from charging and excitation of a cat's hypothalamus to trigger aggression. A striking case of violent human behavior is then linked to a brain lesion — the surgical removal of which restored normal emotional control 70 -- Tickling Midbrain Forebrain Structures Thalamus Limbic system Hippocampus Amygdala Hypothalamus Cerebrum Cerebral cortex Lobes Hindbrain Structures Brainstem Medulla Cerebellum Pons