Module 11: Studying the Brian and Older Brain Structures
advertisement

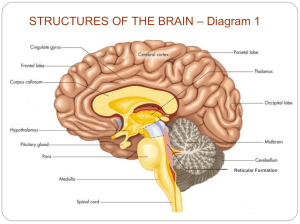
MODULE 11: STUDYING THE BRIAN AND OLDER BRAIN STRUCTURES Unit 3 11.1 How do neuroscientists study the brain connections to behavior and the mind? • Most info known about the brain has been learned thru case studies • Also lesioning: destroying tiny clusters of brain cells • EEG: Use electrodes to measure electrical waves • CT: x-ray of the brain or other soft tissues Cont. • PET Scan: shows actual activity in the brain by the brain’s use of radio-active glucose (brain=sugar hog!) • MRI: provides the best picture • fMRI: will show the brain’s functioning as well— blood flow **should be skeptical of these three. What is normal/abnormal functioning? 11.2 What structures make up the brainstem, and what are the functions of brainstem, thalamus, and cerebellum? Older Brain Structures • Brainstem • Oldest (innermost) region • Controls automatic survival functions • Medulla: controls heart beat and breathing • Pons: coordinates movement (with cerebellum) *brainstem is the crossover point where neurons switch from left side to right side of brain Older Brain Cont. • Thalamus: sits on top of brainstem • Receives info from all senses EXCEPT smell • Routes this info to higher brain centers • Also relays messages from “higher” brain to medulla and cerebellum • Reticular Formation: filters sensory stimuli and relays to other brain areas • Helps control AROUSAL Older Brain Cont. • Cerebellum: nonverbal learning and memory • Time judgment and modulates emotions • Coordinates voluntary movement (with pons) *All of these formations (older brain) work outside our awareness Limbic System • Lies/operates between old and new brain— emotion and drives 3 Structures 1. Amygdala: 2 clusters that deal primarily in aggression and fear (also in learning) 2. Hypothalamus: controls bodily maintenance— pituitary and hormones • Hunger • Thirst • Body temp • Sexual drives • Pleasure centers (animals) reward centers (humans) • Nucleus accumbens: in front of hypothalamus; dopamine related reward center 3. Hippocampus: process conscious memories *load new memories into long term memory