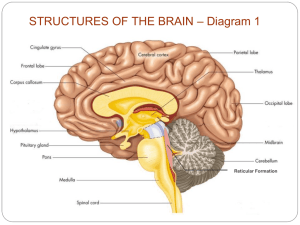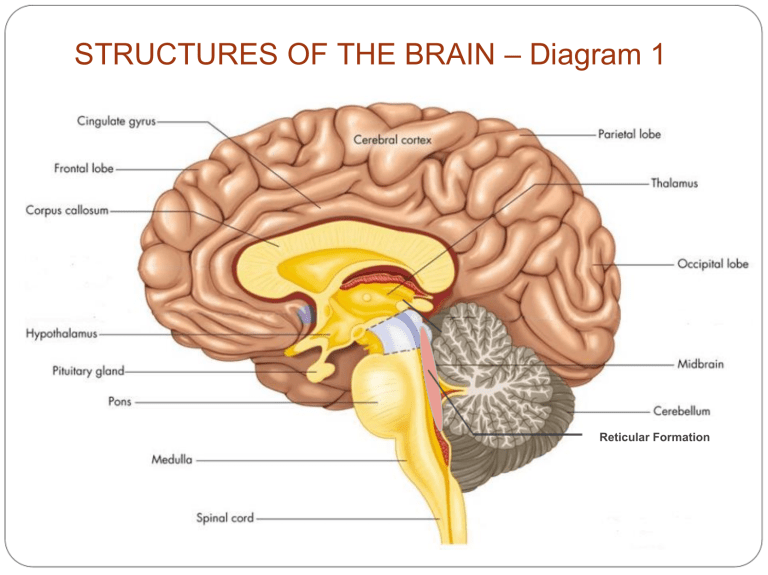
STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN – Diagram 1 Reticular Formation STRUCTURES OF THE BRAIN – Diagram 2 Older Brain Structures Brainstem the oldest part of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells and enters the skull. Responsible for automatic survival functions. Brain Stem Medulla: base of the brainstem, controls vital functions like heartbeat and breathing. Reticular Formation: a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal & involved in attention and sleep (filtering out stimuli) Brain Stem Thalamus: the brain’s sensory switchboard --directs messages to the sensory areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla. Pons: bridge between the brain and spinal cord (especially dealing with motor messages) and/or sleeping (sleep cycle) Cerebellum The “little brain” attached to the rear of the brainstem. It helps coordinate voluntary movements and balance. The Limbic System Limbic System a doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebrum, associated with emotions such as fear, aggression and drives for food and sex. It includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus. Limbic System Amygdala: two almondshaped neural clusters linked to emotion of fear and anger. Hippocampus: two fingerlike structures attached to amygdala involved in processing (new) memories Limbic System Hypothalamus: lies below (hypo) the thalamus; directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking, body temperature, and sex. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. Ventromedial – “vomit” – tells you when to STOP eating Lateral – “let’s eat” – tell you when you are hungry The Cerebral Cortex The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres. The body’s ultimate control and information processing center (higher order thoughts). Corpus callosum: band of nerves that connect the two cortical hemispheres & carries messages between them