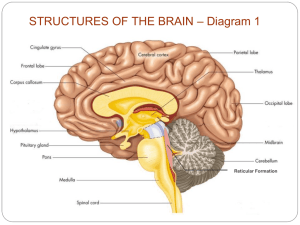
LIMBIC SYSTEM Department of Physiology, Kursk State Medical University Kartisha Poobalan – Group 27 ( 2 nd year 3 rd Semester ) Table of contents 1. Definition & Function 2. Components of limbic system : Parts and Functions 3. “Reward’ and ‘Punishment’ Function of limbic system DEFINITION The neuronal circuitry that control emotional behavior and motivational drives FUNCTION BEHAVIOR EMOTION MOTIVATION AL Components ◦ Thalamus ◦ Amygdala ◦ Hippocampus ◦ Hypothalamus ◦ Cingulate Gyrus ◦ Parahippocampal gyrus ◦ Uncus ◦ Subcallosal gyrus ◦ Orbitofrontal cortex Hypothalamus ◦ Major control headquarters of the limbic system ◦ It send the output signals in 3 directions :Downward to the brainstem Upward toward many higher areas of diencephalon and cerebrum Into the hypothalamic infundibulum REPRODUCT IVE INFLUENCE OF EMOTION REGULATE WATER INTAKE ENDOCRINE FUNCTIONS OF HYPOTHALAM US REGULATE FOOD INTAKE AUTONO MIC CIRCADIAN RHYTHM TEMPERATURE REGULATION Amygdala ◦ Window of the limbic system: wide aff and eff connections with visual and auditory association areas. ◦ Controls of fear and anxiety ◦ Control sexual desires ◦ Help to pattern the person’s appropriate behavioral response Hippocampus ◦ Forming new memories ◦ Provide long term memory ◦ Stimulation cause different behavioral patterns ◦ Hyperexcitable Cingulate gyrus coordinates sensory input with emotions emotional responses to pain maternal bonding regulates aggressive behavior language expression communication decision making Parahippocampal gyrus Important role in spatial memory and navigation Uncus Concerned with smell and taste. Disease of this area can produce hallucination of foul smell Orbitofrontal cortex Subcallosal gyrus Important role in development of major depression Important role in conflict resolution Involved in stimulus-reward and stimulus-outcome association ‘REWARD’ & ‘PUNISHMENT’ FUNCTION OF LIMBIC SYSTEM Reward Centers ◦ Located in - Lateral nuclei of the hypothalamus - Ventromedial nuclei of the hypothalamus ◦ Less potent in :- Hypothalamus - Septum - Amygdala - Certain areas of the thalamus - basal ganglia - extending downward into basal tegmentum of the mesencephalon Punishment Center ◦ Areas for punishment and escape tendencies 1. Central gray area surrounding the aqueduct of Sylvius 2. Mesencephalon and extending upward 3. Periventricular zones of the hypothalamus and thalamus 4. Amygdala and Hippocampus ◦ Shows signs of displeasure, fear, terror, pain, punishment and even sickness ◦ Inhibits reward and pleasure centers completely THANK YOU