carbon - Falmouth Schools
advertisement

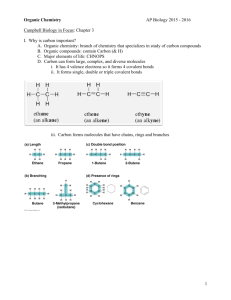
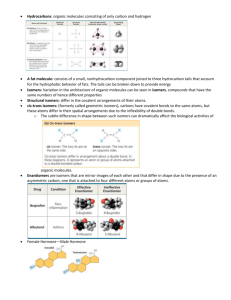
Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Chapter 4 • Organic molecule - molecule contains carbon. • Living things also composed of other elements (i.e. hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), sulfur (S), and phosphorus (P)) • Carbon - 6 electrons (2 in first shell, 4 in second) • Carbon is therefore likely to form covalent bonds. • Carbon chains form skeletons of most organic molecules. • Hydrocarbons - organic molecules that consist of only carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Fats - long hydrocarbon tails attached to a non-hydrocarbon component. Examples of carbon bonding Long hydrocarbon chains • Isomers - compounds that have same molecular formula but different structures and chemical properties. • 1Structural isomers - molecules that have same molecular formula but are different in structure. Butane – both are C4H10 but are set up differently • 2Geometric isomers - same covalent bonds but differ in how electrons are placed. • Usually double-bonded molecules. • Because of double bond, molecules cannot rotate around double bond. Position of “X” prevents the rotation of the molecule. • 3Enantiomers - mirror images of each other (like left and right-hand images) • There has to be 4 different atoms attached to carbon for there to be an enantiomer. Diagram on left cannot be rotated to match diagram on right Functional groups • Functional groups - groups of organic molecules most often used in chemical reactions. • Arrangement of functional groups give molecules their uniqueness. Note difference between male and female hormone • 6 functional groups. • 1Hydroxyl group (-OH) – Polar covalent bonds - increase solubility of molecule. • Contains functional group - alcohol. • 2Carbonyl group (CO) – Oxygen atom joined to carbon skeleton by double bond. • If it is attached to end of molecule - aldelhyde. • If not it is a ketone. • 3Carboxylic group (COOH) – Acts as an acid. • Known as carboxylic acids. • 4Amino group (NH2) - Acts as base. • Known as amines. • 5Sulfhydryl group (SH) – Help stabilize structure of proteins. • Known as thiols. • 6).Phosphate group (PO4) – One function of this group to transfer energy between organic molecules.