1 Organic Chemistry AP Biology 2015
advertisement

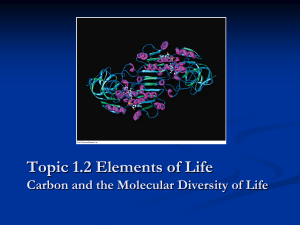
Organic Chemistry AP Biology 2015 - 2016 Campbell Biology in Focus: Chapter 3 I. Why is carbon important? A. Organic chemistry: branch of chemistry that specializes in study of carbon compounds B. Organic compounds: contain Carbon (& H) C. Major elements of life: CHNOPS D. Carbon can form large, complex, and diverse molecules i. It has 4 valence electrons so it forms 4 covalent bonds ii. It forms single, double or triple covalent bonds iii. Carbon forms molecules that have chains, rings and branches 1 iv. Forms isomers - molecules that have same molecular formula, but differ in atom arrangement different structures → different properties/functions Cis-Trans Isomer Structural Isomer Enantiomers (Geometric Isomer) Varies in covalent arrangement Differ in spatial arrangement Mirror images of molecules (different forms known as enantiomers) v. Isomers can have very different biological properties a. Thalidomide = “good” enantiomer: reduce morning sickness “bad” enantiomer: cause massive birth defects “good” converts to “bad” in patient’s body Now used to treat cancers, leprosy, HIV b. Other examples 2 II. Chemical groups - small groups of atoms commonly found on the hydrocarbon backbone of biological molecules. If they are involved in chemical reactions, then they are known as functional groups. A. You need to know: 1. structure of important chemical groups 2. functional properties B. Important chemical groups 3 4