Week 6 Homework
advertisement

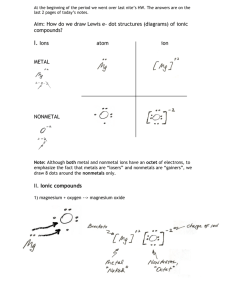
Date _________________ Name ______________________ Section A B C Week 6 Homework Information from the Periodic Table 1. What is the atomic symbol for… a. chromium 2. What is the name of the element… a. Ni b. sodium b. Cl c. zinc c. I d. aluminum d. N e. sulfur e. Si f. oxygen f. Ca g. neon g. Mg h. hydrogen h. Be 3. For each element above in 1 and 2, write the number of protons in parentheses. For example, 1 a. will be Cr (24). 4. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to ____________________________________. 5. List the subatomic particles, their location, size and charge. 6. For the elements below, write the symbol and name of the ion formed. a. Na h. F b. Br i. P c. Cl j. K d. Ca k. H e. Li l. Ne f. N m. Rb g. Al n. Mg 7. What is the trend for charge of an ion on the periodic table? Page 1 of 3 Name ______________________ Section A B C Week 6 Homework Date _________________ 8. Atoms that have lost electrons are called _____________ and have __________________ charges. 9. Atoms that have gained electrons are called ______________ and have ________________ charges. 10. What happens when a positive ion is near a negative ion? Why? 11. Draw a sketch to show the valence electron transfer between the following pairs of elements. The first one has been done as an example. Na Cl Li Ca O Mg Cl Ca Cl Al F S Na Br Br Br K Br O Na Na F Formulae for Ionic Compounds 12. Write the formula for the compound made by the following: a. francium and chlorine b. strontium and oxygen c. magnesium and iodine d. rubidium and sulfur e. aluminum and sulfur f. lithium and bromine g. calcium and fluorine h. barium and oxygen Page 2 of 3 Date _________________ Week 6 Homework Name ______________________ Section A B C i. calcium and chlorine j. magnesium and sulfur k. beryllium and oxygen l. aluminum and iodine Names of Ionic Compounds. 13. For each of the compounds in #9, write the name of the compound. a. francium and chlorine b. strontium and oxygen c. magnesium and iodine d. rubidium and sulfur e. aluminum and sulfur f. lithium and bromine g. calcium and fluorine h. barium and oxygen i. calcium and chlorine j. magnesium and sulfur k. beryllium and oxygen l. aluminum and iodine Page 3 of 3